



















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An overview of the endocrine system, focusing on the structure and function of various endocrine glands and their major hormones. It also covers the chemical structure of hormones and the mechanisms by which they act on target organs through receptor binding.
Typology: Schemes and Mind Maps
1 / 32

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!

























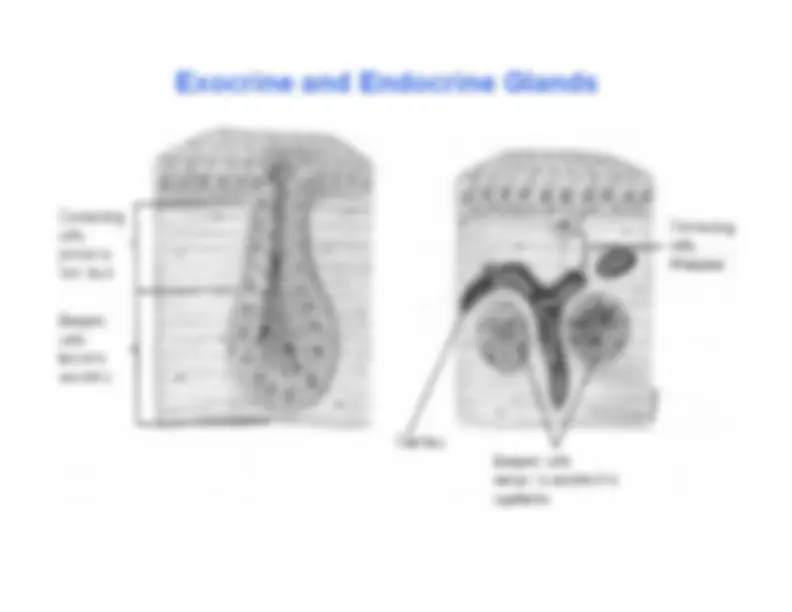
Exocrine and Endocrine Glands
Secrete into a duct and to the outside of a^ body surface Examples:
sweat, tear, saliva Endocrine Glands:
Secrete (hormone) into the blood^ Hormone circulates in blood and acts^ at target organs where hormone receptor^ is expressed Examples:
insulin Exocrine and Endocrine glands:
Mechanisms of Actions of Hormones
-^
-^
Assay and Measurement of Hormones Bioassay Chemical assay Radioimmunoassay (1977 Nobel prize) Receptor binding assay (Scatchard plot)
[hormone] (ng/ml)
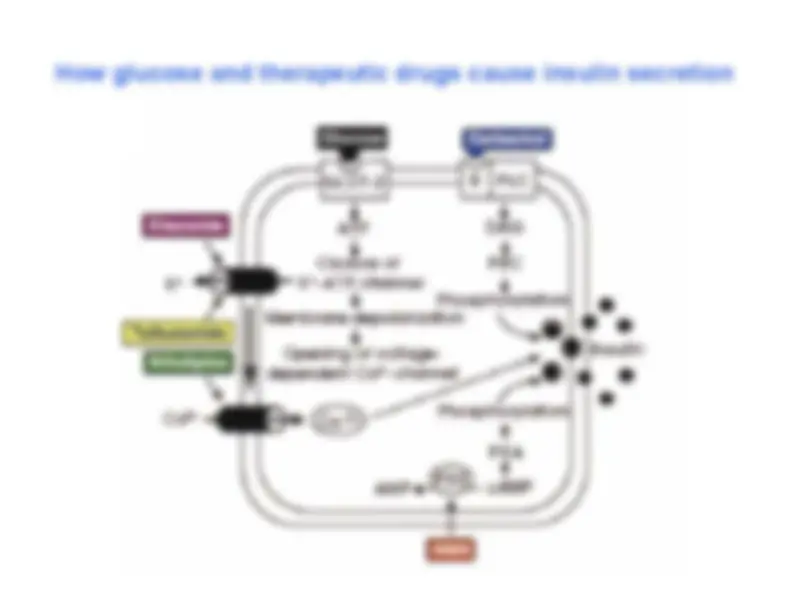
Regulation of hormone secretion: A simple feedback loop^ ↑^ Blood glucose
Two general principles of hormone action^ Acts on cells containing the receptor^ Action is regulated by a feedback mechanism
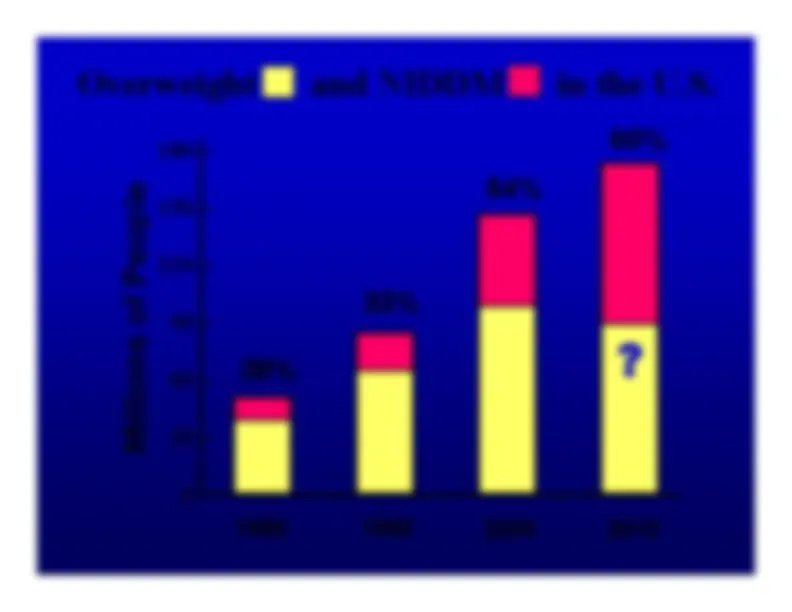
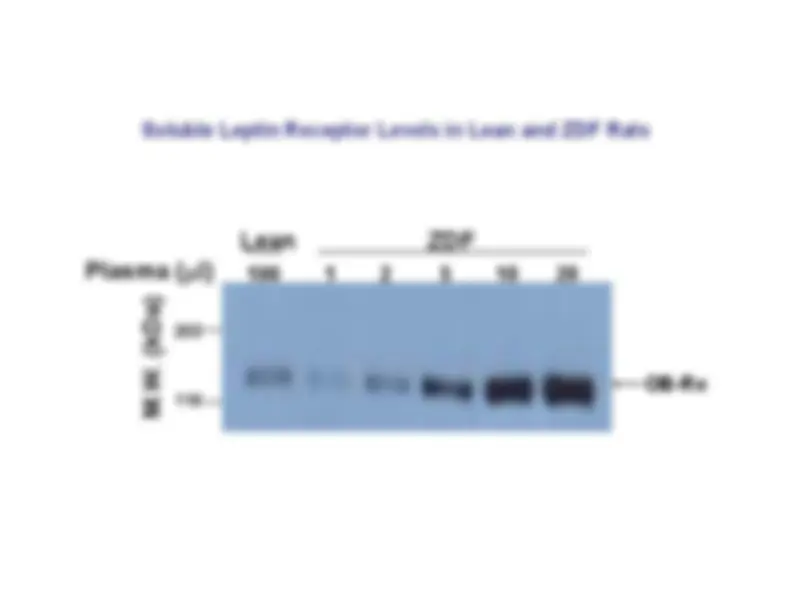
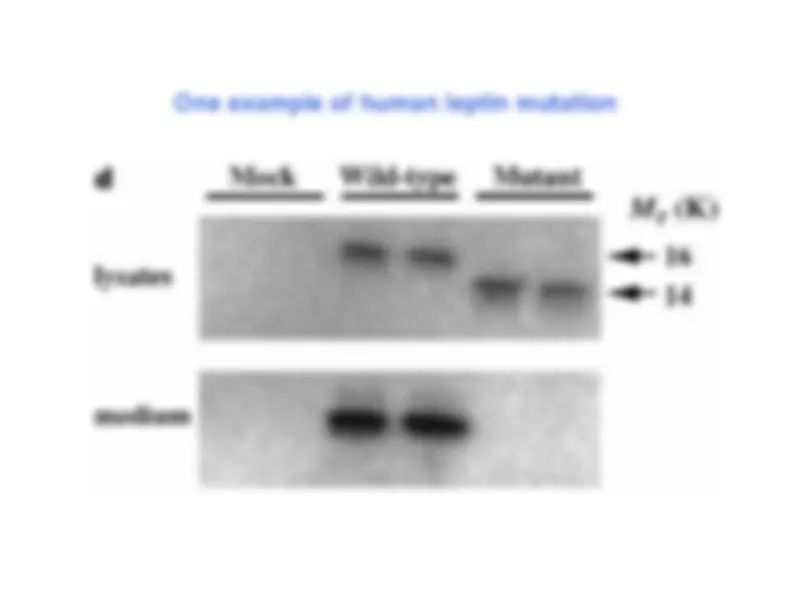
Leptin: a new hormone from fat
Tissue distribution of leptin
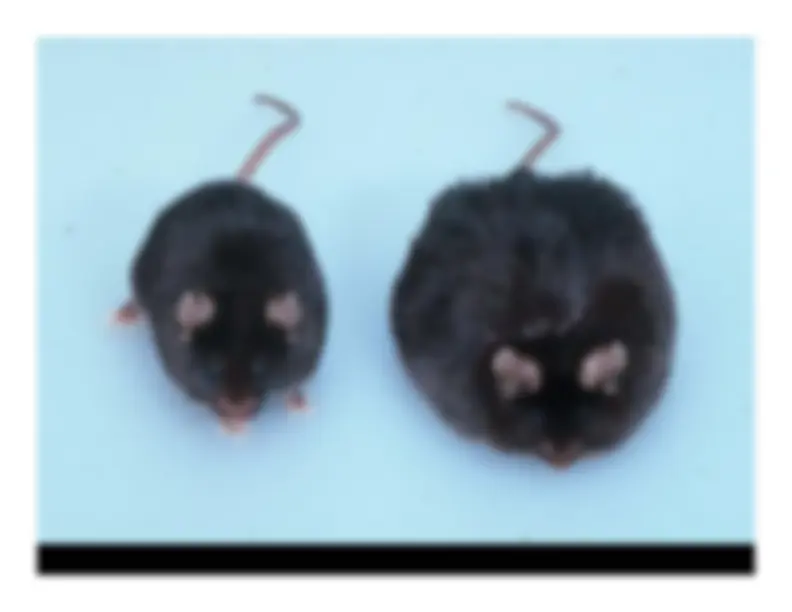
ob/ob^
Leptin Receptor Isoforms
1162 (^894805) Extracellular
TMR Intracellular
892 900