


















































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Coordination Complex Material Type: Notes; Professor: Megehee; Class: ADVANCED INORGANIC CHEMISTRY; Subject: CHEMISTRY; University: St. John's University-New York; Term: Fall 2011;
Typology: Study notes
1 / 108

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





























































































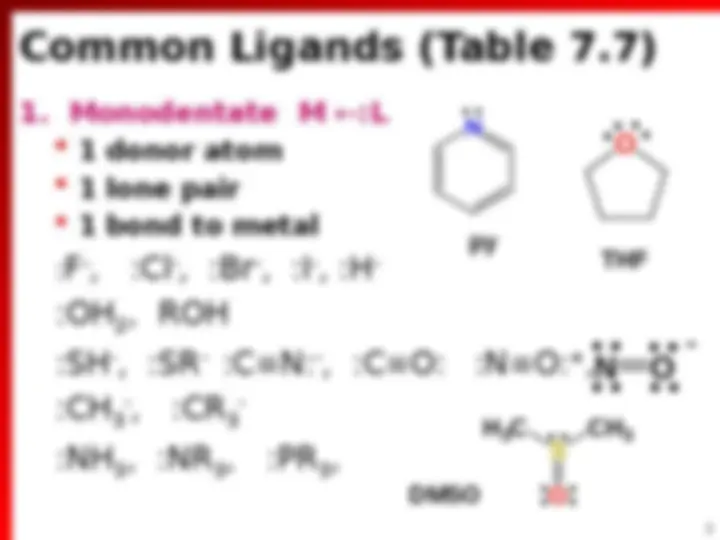
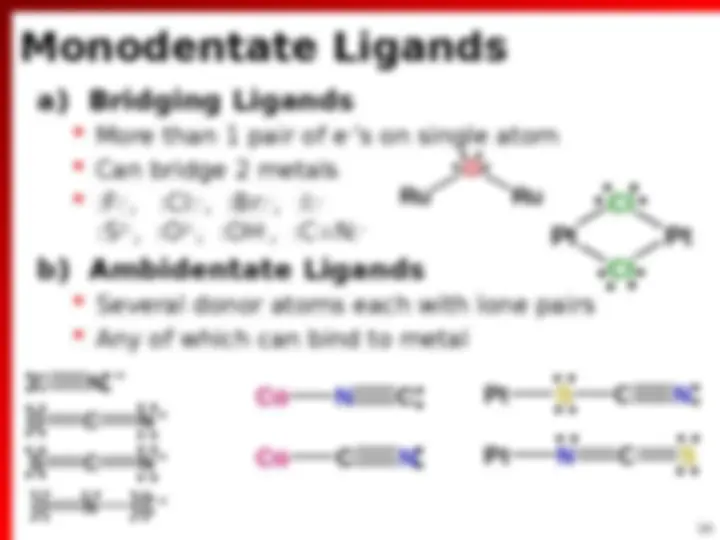
(^) Ions or molecules that donate e ^ pair to metal (^) Lewis base
(^) Lewis Acid (^) Can accept more than 1 Ligand (Lewis base)
(^) = Lewis acid base adduct formation
(^) Central metal atom surrounded by set of ligands. 3+ 2 2
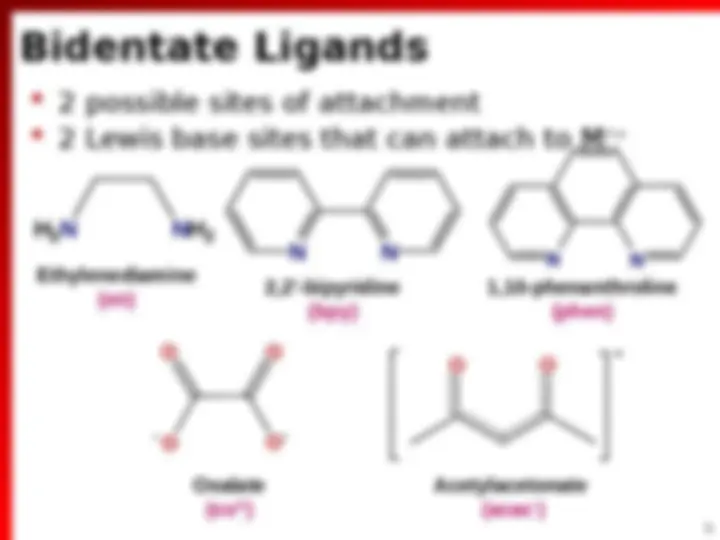
2. Chelate Ligands
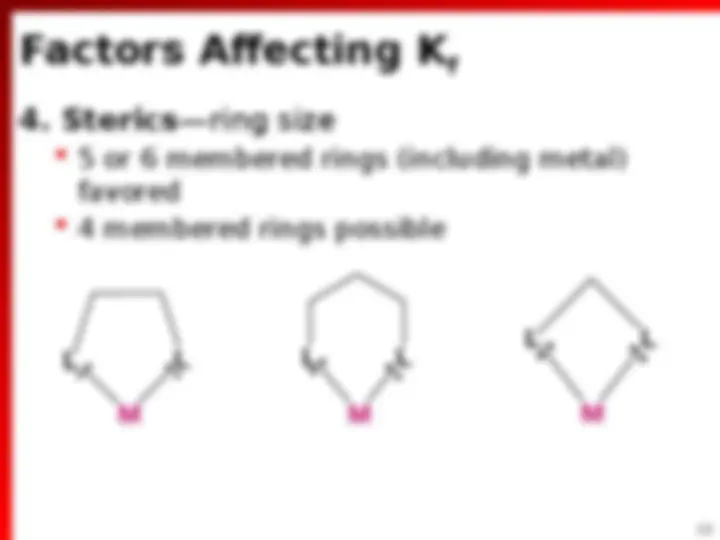
(^) Each of which can simultaneously form 2 e bond to M n+ (^) Usually 5 or 6-membered rings with M (^) Sometime form 4-membered rings (^) Must be nonlinear molecules L L M
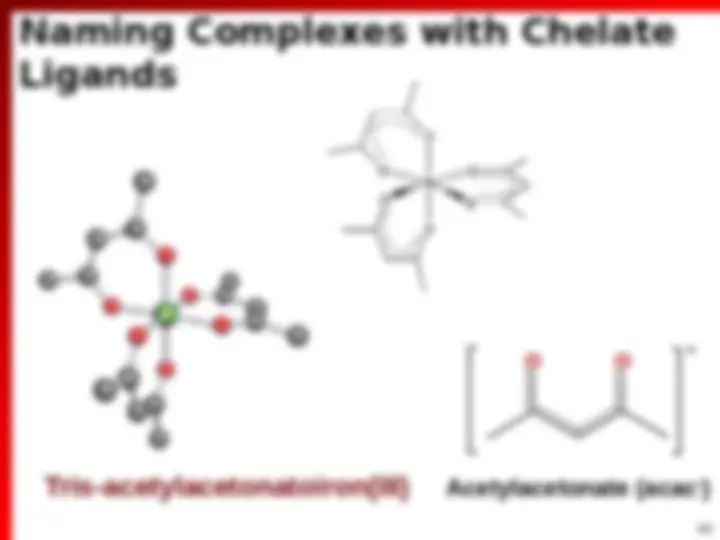
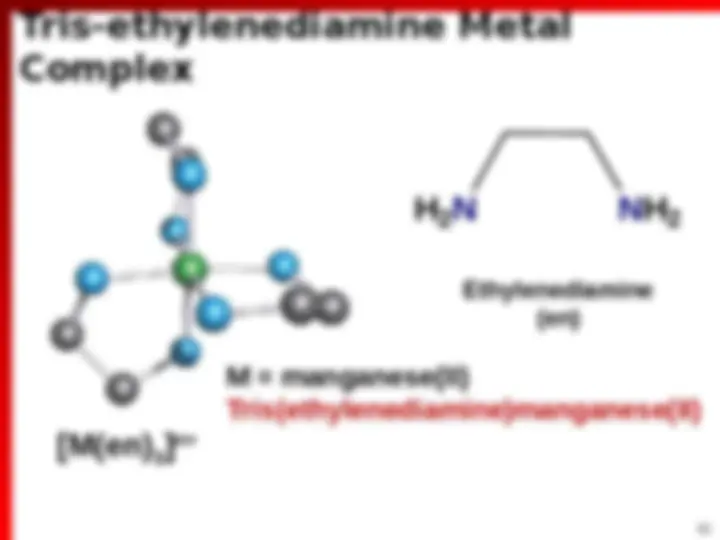
Bidentate Ligands (^) 2 possible sites of attachment (^) 2 Lewis base sites that can attach to Mn+ O O^ N N N N O O O O H 2 N NH 2 1,10-phenanthroline (phen) 2,2’-bipyridine (bpy) Ethylenediamine (en) Oxalate (ox 2 ) Acetylacetonate (acac )
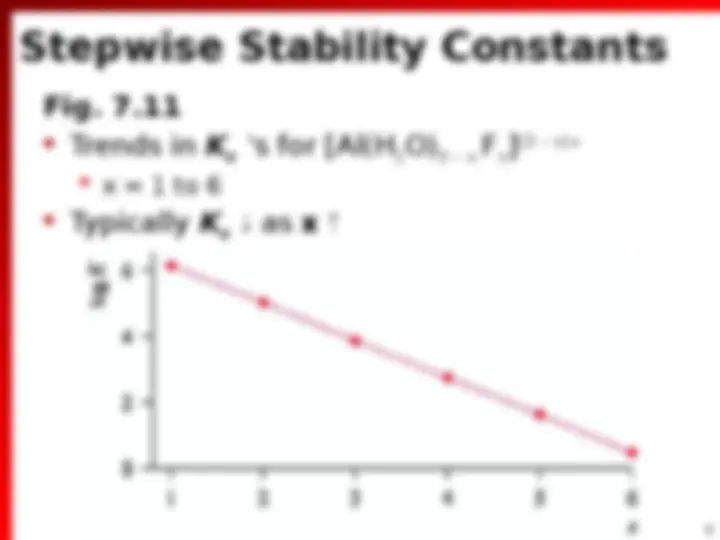
Stability Constants (^) Measure of selectivity of ligand for Metal ion (^) Nature of ligand (^) Coordination geometries common to metal (^) Oxidation state of Metal [M(H 2
6
z+
5
z+
2
5
z+
4
2
z+
2
4
2
z+
3
3
z+
[M][L ] [ML ] K 1 [ML][L ] [ML ] K 2 2 [ML ][L ] [ML ] K 2 3 3
M + L ML M + 2 L ML 2 M + 3 L ML 3 M + n L ML n Overall Stability Constants ( n )
1
1 2 2 2 2
1 2 3 3 3 3
n 1 2 n K K K
Factors Affecting K f
(^) Hard Acids (Fe3+, V3+, Mn3+) (^) Hard Bases (RO , NR 3
(^) Soft Acids (Au+, Cu+, Hg+) (^) Soft Bases (RS , PR 3
(^) Does metal prefer 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, or 8
Factors Affecting K f
f
(^) Once one site bound, other(s) in close proximity (^) most favorable to add (^) Most Biochemical Metal Binding sites are chelating ligands (^) Can stabilize even labile metals (^) K= 10^12 – 10^25
Factors Affecting K f : 3. Chelate (^) G = H T S (^) Contributions from both enthalpy & entropy (^) Entropy easier to understand [Ni(OH 2 ) 6 ] 2+ ( aq ) + 6NH 3 ( aq ) [Ni(NH 3 ) 6 ] 2+ ( aq ) + 6H 2 O( aq ) 7 complex ions/molecules 7 complex ions/molecules (^) S 0 [Ni(NH 3 ) 6 ] 2+ ( aq ) + 3en( aq ) [Ni(en) 3 ] 2+ ( aq ) + 6NH 3 ( aq ) 4 complex ions/molecules 7 complex
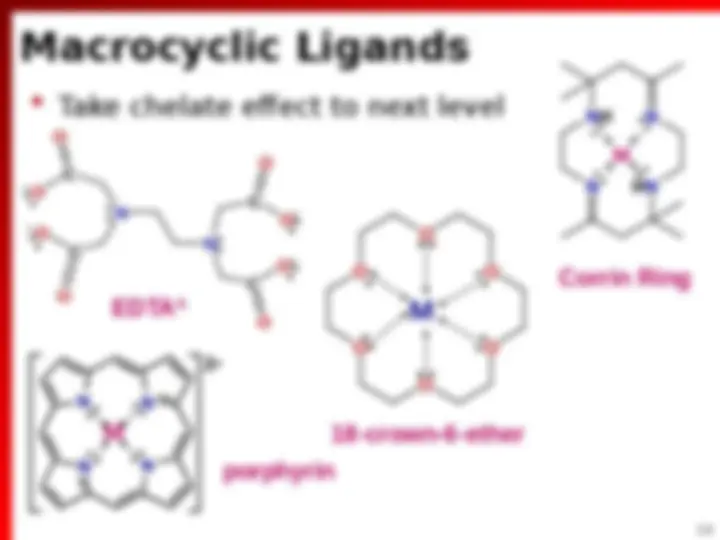
Macrocyclic Ligands (^) Take chelate effect to next level N N C C C C O O O O O O O O N NH HN N Corrin Ring EDTA (^4) N N (^) N N 2 porphyrin O O O O O O 18-crown-6-ether M M M
In Class Exercises
Ag
( aq ) + 2NH 3
3
2
( aq ) log K = 7. Ag
( aq ) + Br
2
( aq ) + Br
Coordination Complexes
(^) Complex ion: [Co(NH 3 ) 6 ] 3+ , [PtCl 4 ] 2 (^) Compound: Ni(CO) 4
Outer Coordination Sphere
(^) there to balance charge only
Complex ion Counterion Outer sphere Complex [Mn(OH 2
6
2+
6
4
[Co(NH 3
6
3+
6 ]Cl 3 [PtCl 4
2
= Na 2 [PtCl 4
(^) For ionic complexes name (^) Cation first, anion second (^) Put space between names of complex ion & counterion