



Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
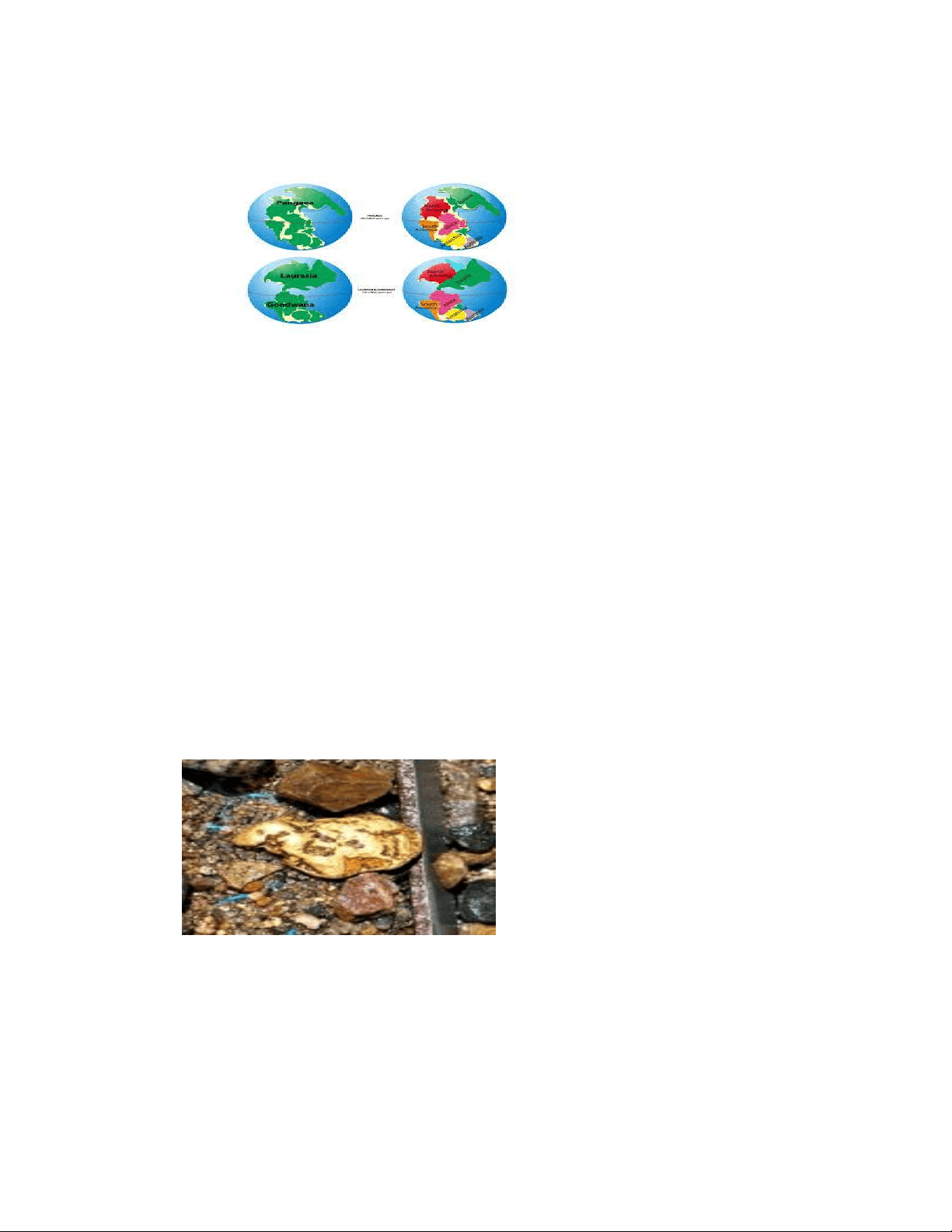
Alfred Wegener (1912) proposed the theory saying large PANGEA splitted into many smaller pieces to make today's continents.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 4

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!



Continents cover 29 percent of the surface of the earth and remainder is under oceanic waters. Alfred Wegner was a German meteorologist who put forth the Continental Drift
Theory in 1912.
It is considered that there was a single landmass called PANGAEA- which means all earth. The mega-ocean is called PANTHALASSA – which means all water.
The basic argument was that – About 200 million years ago, the mega-landmass PANGAEA started splitting into two large landmasses namely, LAURASIA in the north and GONDWANALAND in the south. These two landmasses kept splitting till they they reached present configuration of continents and oceans.
The argument for the C ontinental Drift Theory gets strength from the following evidences:
Placer Deposits
landmasses of Southern Hemisphere. Thick tilliation at base shows prolonged glaciation. Counterparts of this succession are found in Africa, Falkland island, Madagascar , Antarctica and Australia besides India. It proves paleoclimates and drifting of continents. These landmasses have similar histories.
Brazil show that obviously gold deposits of Ghana are derived from Brazilian plateau when they were together.
According to Wegener, forces responsible for this Continental drifting are:
Post drift studies have shown some progress with following noteworthy points:
Convectional current Theory: Arthur Holmes in 1930s discussed the possibility of convection currents operating in the mantle portion. These currents are generated due to radioactive elements causing thermal differences in the mantle portion. Mapping of the oceanic floor: Dating of rocks from oceanic crust reveal that they are much younger than continental areas.
Tectonic plate/ lithospheric plate is a massive , irregularly shaped slab of solid rock , generally composed of continental and oceanic lithosphere. Plates move horizontally over the aesthenosphere as rigid units. these can be called oceanic or continental based on which area is major on the plate. Theory of plate tectonics proposes that – Earth lithosphere is divided into seven major and some minor plates.
Sites of pulling away : Spreading sites. Example, Mid-Atlantic Ridge, at this the American Plate is /are separated from the Eurasian and African Plates.
II. Convergent Boundaries:
Where crust is destroyed as one plate dived under another. The location where sinking of plate occurs is- Subduction zone. Three ways of convergence are: a) between oceanic and continental plate; b) between two oceanic plates; c) between two continental plates.
II. Transform Boundaries:
Crust is neither produced, nor destroyed as the plates slide horizontally past each other. Transform faults are the planes of separation generally perpendicular to mid-oceanic ridges. Since eruption is irregular, differential movement of a portion of plate away from axis of earth. Also, rotation of earth has its effect on separated blocks of plate portions.
Rates of plate movements determined by the strips of normal and reverse magnetic field that parallels the mid-oceanic ridges.
Heat within earth comes from two sources –
The slow movement of hot, softened mantle that lies below the rigid plates is the driving force behind the plate movement.