













Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
This lecture from computer networking for engineers, taught by jeffrey miller, covers the progression of telephone networks from fully connected to multi-level switch connected, the structure of telephone networks including local loops, trunks, and switching offices, the challenges of transmitting digital signals over telephone lines, and the use of modems and dsl for digital service. The lecture also touches on multiplexing techniques and switching types.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 20

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!













th^
-^
Local Loops–
Analog twisted pairs going into buildings
-^
Trunks–
Digital fiber optics connecting switching offices
-^
Switching Offices–
Calls are moved from one trunk to another
-^
The square waves (DC) used in digital signals have a wide frequency spectrum, subjecting them toattenuation and delay distortion
-^
With telephone lines, AC signaling is used–
A continuous tone between 1000-2000Hz is used with different types of modulation to represent the
yp
p
binary values
-^
The number of samples per second is measured in baud – an n baud line transmits n symbols/second^ Binary SignalBinary
Signal
Amplitude Modulation Frequency Modulation
Phase Modulation
DSL is the phone company’s way of offering digital service over thelocal loop
-^
The capacity of the local loop depends on length, thickness, andThe capacity of the local loop depends on length, thickness, andgeneral quality
-^
The following graph shows the bandwidth versus distance over a Cat-3UTP for DSLUTP for DSL
-^
-^
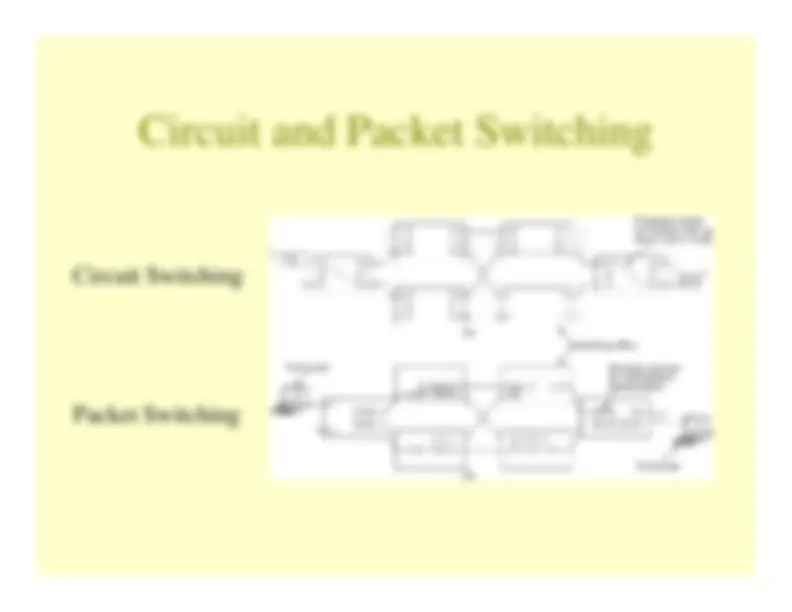
Circuit switching is used primarily with voice conversations–
When a voice conversation is initiated, the switching equipment within thetelephone system needs to find a physical path from your telephone to thereceiver’s telephone
Message switching is used primarily with data–
When the sender has a block of data to send, it is stored in the firstswitching office and forwarded one hop at a time (called a store-and-forward network)
-^
Message switching has no limit to the size of the data though, so lines canb^
ti d
f^
l^
i d
f ti
be tied up for long periods of time
Packet switching is used primarily with data–
Packet switched networks have an upper limit on the block size, allowingpackets to be buffered in router main memory rather than on disk at thepackets to be buffered in router main memory rather than on disk at therouter
-^
This allows the handling of interactive traffic