










Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Three theoretical perspectives on classism: functionalism, symbolic interactionism, and conflict theory. Functionalism explains how certain jobs are considered more prestigious due to their importance and the rewards they offer. Symbolic interactionism argues that social class is determined by talent and effort. Conflict theory, based on Marx's ideas, emphasizes class struggle and inequality. examples, discussions, and video clips to illustrate these theories.
What you will learn
Typology: Slides
1 / 17

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!










Functionalism in Classism
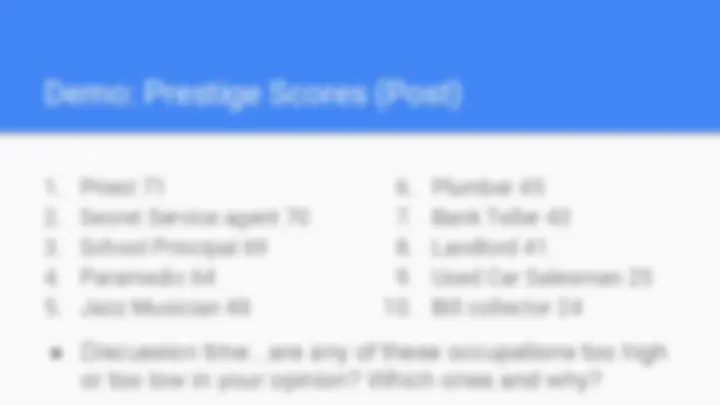
● Discussion time...are any of these occupations too high
Functionalism in the Demo
Video Clip: Fresh Prince of Bel Air (Pre)
Video Clip: Fresh Prince of Bel Air (Post)
○ The frat leader claims that Carlton has had it easy (this rejects S.I.) ○ Carlton’s father, Philip Banks, states he has “worked very hard to give his family a good life” which highlights the theory of S.I. ○ S.I. in classism = people become successful based off talent and effort as Philip has done for his family
Video Clip: The Sneetches (Pre)
Video Clip: The Sneetches (Post)
Social Classes in America
● Class consciousness: sense of identification with the goals and interests of the members of a particular social class
Upper Class: Investors, heirs, CEOs
Upper Middle: Upper Level Managers, professionals, owners of businesses
Middle Class: Lower Level Managers, semiprofessionals, non-retail salesmen
Working Class: Low paid manual, clerical, craft, retail sales workers
Working Poor: Lowest paid manual, retail, service workers
Underclass: unemployed, part time, public assisstance
Poverty in America
● Absolute poverty - absence of enough money to secure life’s necessities ● Relative poverty - comparison of bottom portion of society to the rest ● 12.7% of American population is poor (37 million people) ● Most people in poverty come from identifiable groups ● African Americans and Latinos make up nearly half the poverty population ● When females head the family, chances of poverty rise greatly ● 18% of children under the age of 18 are in poverty (highest rate for any group in the US) ● Feminization of poverty - the idea or trend that females and children make up the majority of our nation’s poor ● Reasons as to why women tend to be in poverty more than men: ○ Women earn $.80 for every $1 men earn ○ Lack of good childcare facilities ○ Women with kids find it harder to maintain employment
Social Mobility
Social Mobility is the movement of people between social classes. Types of Mobility: ● Vertical Mobility ○ Change in social status ○ Two directions; Upward Mobility and Downward Mobility ○ Downward Intergenerational Mobility happens more frequently today (Newman,
○ Possibly due to outsourcing ○ Downwardly Mobile people tend to experience negative psychological effects ● Horizontal Mobility ○ Change in occupation without any change in social status ● Intergenerational Mobility ○ Mobility is Vertical or Horizontal over a generation
Social Mobility (cont.)
Social Systems: ● Caste System ○ Individuals are born unto a social class permanently ○ Social Mobility does not occur ○ Marriage is limited to individuals in the same caste ○ India is divided up to 5 classes; from priests and scholars to the “untouchables” ○ The power wealth and prestige of the upper classes keep the system intact ● Open Class System ○ Individual’s social class is based on merit and effort ○ Social Mobility is enabled ○ U.S. is relatively open class