Partial preview of the text
Download Class D Water License – Texas Exam Questions & Answers| 100% Success and more Exams Water and Wastewater Engineering in PDF only on Docsity!
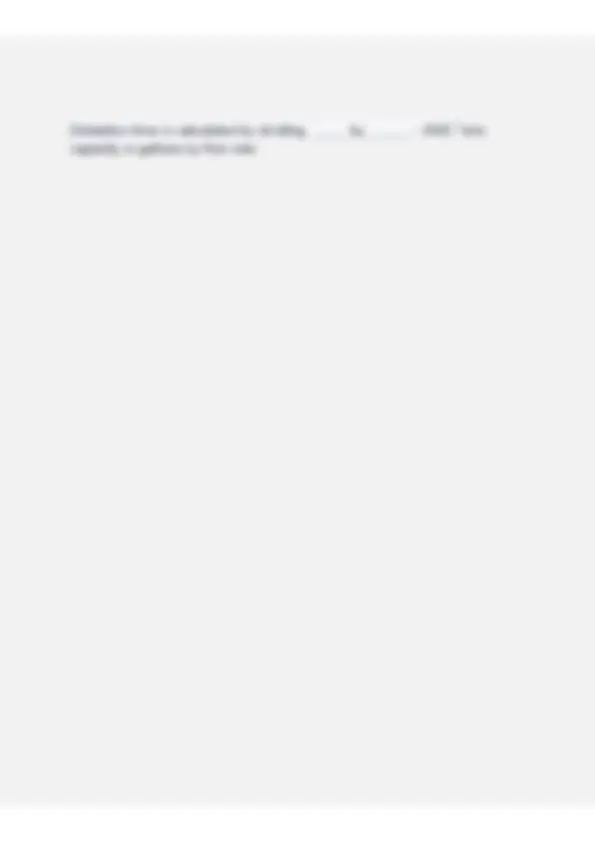
Class D Water License — Texas Exam Questions & Answers| 100% Success Operators have a responsibility to provide drinking water that meets federal and state standards. (true/false) - ANS-true Water must be disinfected, delivered at inadequate pressure, and be ample in quantity. (true/false) - ANS-false (adequate pressure) Utility employees should guard the water supply and facilities from contamination, public tours, and even terrorism. (true/false) - ANS-false (public tours) The state requires bacteriological sample results be kept years. - ANS-5 years The state requires chemical analysis be kept at least years. - ANS- 10 years EPA requires a water system to keep a copy of each consumer confidence report at least years. - ANS-5 years A public water system provides the public with piped water for human consumption, serves at least service connections, and regularly serves at least individuals daily at least days out of the year. - ANS-15 service connections 25 individuals 60 days out of the year The water utility field affects everyone because . - ANS-water is essential to life and health The water utility employee should remember customers are entitled to and . - ANS-courteous treatment and answers to questions about water In Texas, water operator licensing is administered by the .- ANS- TCEQ All public water systems are required to employ licensed operators even if the system only treated water bought from another source. - ANS-redistributes treated water Public water systems include cities, municipal utility districts, rural water supply corporations, mobile home parks, and . - ANS-campgrounds Examples of community water systems include a. municipalities b. municipal utility districts c. rural water supply corporations d. mobile home parks e. all the above - ANS-e. all of the above A federal agency impacting the water utility industry is the . - ANS- EPA The most important federal law impacting the water utility industry is the . - ANS-Safe Drinking Water Act (PL93-523) The four national safety and quality standards for drinking water covered in the Safe Drinking Water Act are physical, chemical, and radiological. - ANS-bacteriological The state agency that regulates drinking water in Texas and administers the federal Safe Drinking Water Act is the .- ANS-TCEQ Water utility system personnel are required to notify the TCEQ of changes or alterations of the system, a new facility to be built, and water supply . - ANS- health hazards a. departments to call for service b. explanations of utility policy c. a history of the utility d. tips on water conservation e. all the above - ANS-e. all of the above Delinquent payment notices should be a. tactful and tasteful b. mailed in an envelope c. businesslike d. all listed - ANS-d. all listed EPA requires community water systems to provide customers with a report on the system's water quality. - ANS-yearly If water quality reports are attractive and easy to , they can build goodwill and trust with the customer. - ANS-understand Good treatment of employees includes fair wages, benefits, and working conditions. - ANS-safe working conditions Follow up with a phone call or to make sure everything is satisfactory. a. postcard b. email c. letter d. a and b - ANS-d. postcard or email Listen to special requests and seek solutions to oblige the customer within .- ANS-utility policy Treat customers as though another water utility across the street is competing for your . - ANS-customers The molecular formula for water is .- ANS-H2O0 Water occurs in three forms: solid ice, liquid water, and water vapor. (true/false) - ANS-true The is the natural exchange of water between the earth and the atmosphere. - ANS-hydrologic cycle Average water use depends on temperature, rainfall, cost, supply, and economic level. (true/false) - ANS-true Groundwater is located above the earth's surface and tapped by wells. (true/false) - ANS-false (groundwater is below the surface) water comes from rivers, lakes, and reservoirs. - ANS-Surface Future water supplies will become more plentiful according to the TCEQ. (true/false) - ANS-false Surface water or groundwater prior to treatment is called water. - ANS-raw water water means the water is free of disease-causing organisms, has a chlorine residual, and is safe for human consumption. - ANS-Potable must be notified about changes to public water systems involving water source, water quality, and health hazards. - ANS-The state Before starting construction, the utility must submit engineering plans to the AWWA. (true/false) - ANS-false (plans must be submitted to TCEQ) Operators must keep records of water usage, system pressure, sample results, chlorine use, repairs, and maintenance. (true/false) - ANS-true Surface water systems must mail reports to the TCEQ in Austin by the Sth of the following month. (true/false) - ANS-by the 10th Water is always found pure in nature. (true/false) - ANS-false Physical characteristics of water are temperature, turbidity, color, taste, odor, and pH. (true/false) - ANS-false (pH is a chemical characteristic) The quality standard for public water supplies is based on the use of water for .- ANS-drinking One of the most important purposes of a public water supply is a. swimming b. landscape watering c. car washing d. firefighting - ANS-d. firefighting Organic matter includes a. sand b. plants, animals and humans c. minerals d. all listed - ANS-b. plants, animals and humans The most important treatment process is , which destroys disease-causing organisms. a. filtration b. disinfection c. softening d. fluoridation - ANS-b. disinfection Public water systems are required to compile a monthly report showing a. rate increases b. accidents c. dates of dead-end flushing d. disciplinary action - ANS-c. dates of dead-end flushing Most groundwater is relatively free of suspended matter, but can be a major problem in surface water. - ANS-turbidity Color in a public water supply should be less than units. - ANS-less than 15 units Chemical characteristics of water include hardness, pH, solids, and .- ANS-gases Water is considered hard when it exceeds mg/L of calcium carbonate. - ANS-100 (may vary depending on who you talk to) A gallon of water weighs pounds and 1 mg/L equals one - ANS-water weighs 8.34 pounds 1 mg/L equals one part per million Hydrogen sulfide is heavier than air, colorless, flammable, toxic, and has a odor. - ANS-rotten egg (unless you get a dose that's so heavy it numbs your sense of smell) Excessive nitrates in drinking water can cause syndrome in infants. - ANS-blue baby syndrome Excessive amounts of fluoride may cause or staining of teeth. - ANS-mottling Trinalomethanes and haloacetic acids are byproducts of chlorination and may increase risk. - ANS-cancer The action level for copper is mg/L and for lead it is mg/L. - ANS-copper is 1.3 mg/L lead is 0.015 mg/L are underground, water-bearing formations yielding useful quantities of water. - ANS-Aquifers The quantity of water a formation yields depends on the thickness and of the formation. - ANS-permeability Problems caused by are declining water levels and subsidence. - ANS-overpumping Well, and cementing protect the well from collapse and surface contamination. - ANS-Well casing The purpose of the well screen is to keep out birds and insects. (true/false) - ANS-false (the well screen keeps out sand; the well vent screen keeps out birds and insects) The most important feature of the well screen is the length. (true/false) - ANS-false (the mesh size is the most important feature) Underground fuel tanks and septic drainage fields must be at least feet from a public well. - ANS-150 feet Feedlots, sewage treatment plants, and landfills must be at least feet from a public well. - ANS-500 feet A well may be developed by surging, overpumping, jetting, and .- ANS-backwashing To disinfect a new well, a chlorine dosage of at least mg/L of chlorine is required. - ANS-50 mg/L Changes in well water levels or the volume of water produced can alert the operator to a drop in the water table, screen stoppage, or damage to the .- ANS-pump Common deep well pumps include the and the vertical turbine. - ANS-submersible Gases such as methane, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen sulfide are reduced by . - ANS-aeration Water from rivers, lakes, and reservoirs is called . - ANS-surface water % of public water systems use surface water. - ANS-40% Boat ramps, marinas, and docks should not be located within feet of a water intake. - ANS-1,000 feet Surface water contains bacteria, algae, and turbidity, but is low in minerals, gases, and dissolved solids. (true/false) - ANS-true The objectives of water treatment are protecting of public health, supplying an aesthetically pleasing product, and . - ANS-protecting consumer property The requires surface water to have pretreatment, pre-disinfection, taste and odor control, coagulation, sedimentation, filtration, covered storage, and terminal disinfection. - ANS-TCEQ Methods for controlling taste and odor problems are , algae control, aeration, chemical oxidation, and activated carbon. - ANS-lake destratification One of the causes of taste and odor problems is and .- ANS- algae and bacteria Coagulants are sodium aluminate, aluminum sulfate, ferrous sulfate, and sodium chloride. (true/false) - ANS-false (sodium chloride is table salt) cause small particles in water to clot together forming floc, and this process, flocculation, forms larger particles that settle more readily. - ANS- Coagulants tests help the operator determine the chemical and dosage to apply. - ANS-Jar tests Turbidity, pH, temperature, alkalinity, and chemical dosage affect . ANS-coagulation To remove suspended solids and chlorine-resistant microorganisms, surface water must be disinfected. (true/false) - ANS-false (it must be filtered) is the final step in removing suspended matter and chlorine-resistant microorganisms. - ANS-Filtering A common filter is the slow sand filter, having several layers of differently sized media. (true/false) - ANS-false (the rapid sand filter) A filter must be when a head loss of 6 to 10 feet occurs. - ANS- backwashed Most surface water is low in minerals, gases, and a. algae b. turbidity A common filter problem is , prevented by proper backwashing. - ANS-mud balls Chemicals used in disinfection are chloramine, chlorine, chlorine dioxide, and . - ANS-ozone Disinfection destroys disease-causing microorganisms called . ANS-pathogens Disinfection destroys pathogens without sterilizing the water. (true/false) - ANS-true Waterborne pathogens live and grow in the intestines of infected people. (true/false) - ANS-true fecal matter entering a water supply transmits pathogens to healthy people. - ANS-Infected Some diseases transmitted by unsafe water include typhoid, dysentery, cholera, measles, polio, and cryptosporidiosis. (true/false) - ANS-false (measles is not transmitted this way) Each water sample is tested for all waterborne diseases. (true/false) - ANS- false (not all) Water samples are tested for microorganisms that indicate contamination. - ANS-fecal contamination The total coliform group of viruses are the indicators of fecal contamination. (true/false) - ANS-false (bacteria, not viruses) Fecal coliform lives in the of humans and warm-blooded animals. - ANS- intestines The presence of fecal coliform in a water sample indicates intestinal waste is in the sample, but there is no risk of disease. (true/false) - ANS-false The number of water taps served by the system determines the minimum number of bacteriological! samples. (true/false) - ANS-false (the population determines the number) The purpose of the sample siting plan is to assure bacteriological samples are taken from vacant houses. (true/false) - ANS-false (vacant houses are not ideal sampling sites as they may sit empty for long amounts of time) is put into bacteriological sample bottles to dechlorinate the water. - ANS-Sodium thiosulfate Before taking a bacteriological sample, you should . - ANS-flush the service line The bacteriological sample bottle should be completely filled with sample water. (true/false) - ANS-false (only fill 100 ml unless the lab tells you otherwise) The monthly bacteriological sample should be marked "construction." (true/false) - ANS-false (it should be marked routine) Get bacteriological samples to the lab within hours or they are rejected. - ANS-30 It is possible to have positive bacteriological samples removed from your record. (true/false) - ANS-true It is public health risk if a positive fecal coliform repeat sample or a positive total coliform repeat sample follows a positive fecal coliform routine sample. - ANS-an acute Acute violations require public notification within 72 hours by radio and television using the words "Minor Health Concern." (true/false) - ANS-false (it's a major health concern) In the event of low distribution pressure (below psi), water outages, repeated unacceptable microbiological samples, or failure to maintain adequate chlorine residuals, special precautions must be instituted by the water system. - ANS-20 psi In Texas, all public water systems are required to have facilities. a. ozonation b. chlorination Gas chlorinators use a rotameter to meter chlorine in or grams/hr. - ANS-Ibs/day Dosage is the amount of chemical applied, demand is the amount of chemical used up, is the amount of chemical remaining after reacting with demand. - ANS-residual Minimum chlorine residuals of (free) and (combined) are required in the far reaches of the distribution system. - ANS-0.2 (free) 0.5 (combined/total) The DPD and chlorine reaction turns the water a color. - ANS- pink to red Chlorine and water make two acids: hydrochloric (HCI) and (HOCI). a. hypochlorous b. hypochloric c. hypochlorous d. hydrochloric - ANS-a. hypochlorous A Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus ( ) must be readily available for chlorine rooms. - ANS-SCBA Chlorinator rooms must have -level and -level screened vents. a. window/ceiling b. door/floor c. high/floor d. low/window - ANS-c. high/floor In chlorinator rooms, must be provided to determine the amount of disinfectant used and the amount remaining daily. - ANS-scales EPA requires any private, municipal, or industrial entity storing or using pounds or more chlorine to have a chemical risk management program. a. 2,000 b. 2,500 c. 3,000 d. 3,500 - ANS-b. 2,500 Heat-sensitive pressure relief plugs in chlorine containers melt at about degrees F. - ANS-160 degrees F Hold an open bottle of % ammonium hydroxide under a suspected chlorine leak. - ANS-10% In case of leaks, the best source of help is the . - ANS-supplier After contacting chlorine gas, wash in a safety shower or with .- ANS-a garden hose facilities equalize demand on the water supply. - ANS-Storage allows uniform pump rates, supplies water for firefighting, and provides time for disinfection. - ANS-Storage Ground storage at a surface water treatment plant is called a ANS-clear well The TCEQ requires storage tanks to have covered vents, an airtight cover, overruns, and . - ANS-entry ports If ground storage is the only storage, capacity must be gallons per connection. Otherwise, total storage capacity (elevated storage included) must be gallons per connection. - ANS-200 gallons per connection 200 gallons per connection If a 30-inch diameter access opening is not provided in a storage tank, the primary roof access must not be less than inches. - ANS-30 inches Storage must be painted, disinfected, and maintained according to OSHA standards. (true/false) - ANS-false (AWWA standards) No paint, coating, or wax containing is allowed in storage tanks. - ANS-lead The state requires stored water to have a disinfectant demand. (true/false) - ANS-false (it requires a disinfectant residual) After construction or maintenance of a storage tank, a sample must be taken after filling the tank. - ANS-bacteriological sample If the bacteriological sample from a storage tank is negative, more samples must be taken until two consecutive samples are positive. (true/false) - ANS-false (if negative you're good to go) Critical safeguards of a distribution system include a chlorine residual, adequate pressure, bacteriological sampling, and control. - ANS- cross-connection control The TCEQ requires that distribution pressure never fall below psi, even during emergencies, and normal distribution pressure must be at least psi. - ANS-never fall below 20 psi 35 psi (normal distribution) Material used in water line construction must meet OSHA specifications and should not affect the taste, odor, or quality of the water. (true/false) - ANS-false (AWWA specifications) Plastic pipe must be NSF approved and have an ASTM pressure rating of at least psi or a standard dimension ratio of . - ANS-150 psi dimension ratio of 26 Select pipe on the basis of strength, length carrying capacity, durability, ease of installation, availability, soil conditions, and cost. (true/false) - ANS- false (length shouldn't be a consideration) Prior to January 1, 2014, pipe and fittings containing more than 8.0% lead, or solders and flux containing more than 0.2% lead, are prohibited in a public water supply. (true/false) - ANS-true valves cut off sections of a system. - ANS-lsolating valves solves problems of taste, odor, red water, or bad samples. - ANS- Flushing The meter is the most common design for residential use. - ANS- positive displacement meter Mains must be no closer than feet, in all directions, from sewers or manholes. - ANS-9 feet Trenches for laying six-inch and larger pipe must be at least inches wide and inches wider than the pipe diameter. - ANS-18 inches wide 12 inches wider The top of a pipe in a trench must have at least inches of cover. - ANS-24 inches Do not work in a trench feet or deeper unless it is protected from cave-in. - ANS-5 feet Using timber, plywood, or commercial devices to support an excavation is known as . - ANS-shoring Shoring is not necessary if the trench walls are sloped to the maximum allowable . - ANS-slope Place spoil banks at least feet from the trench excavation. - ANS-2 feet Dose new mains with mg/L or more of chlorine at least hours. - ANS-25 mg/L 24 hours Do not place a main into service until a bacteriological sample is tested with results. - ANS-negative One bacteriological sample is required for each feet of completed main. - ANS-1,000 feet Flushing reduces slime and scale buildup, reduces red water complaints, brings chlorinated water to contaminated areas, and removes materials from the system. - ANS-chlorine-reducing