



























Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
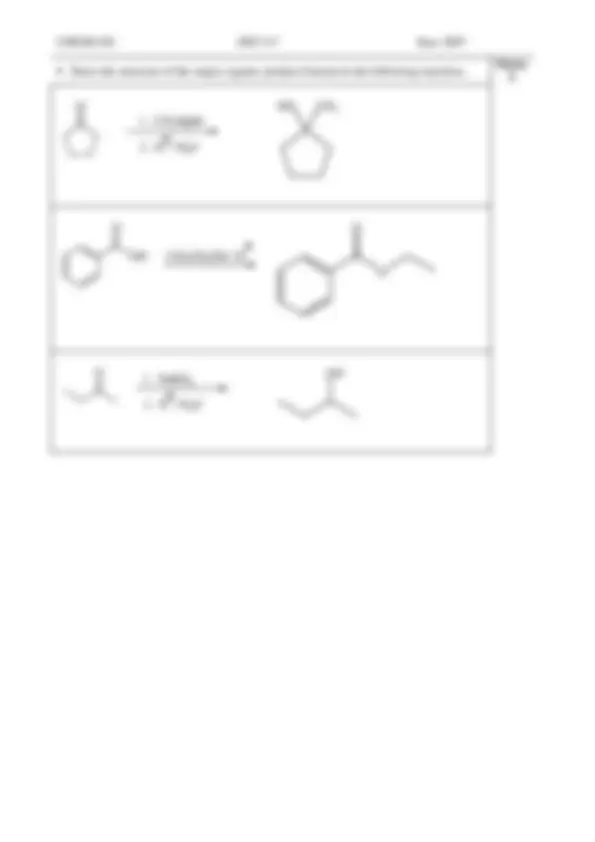
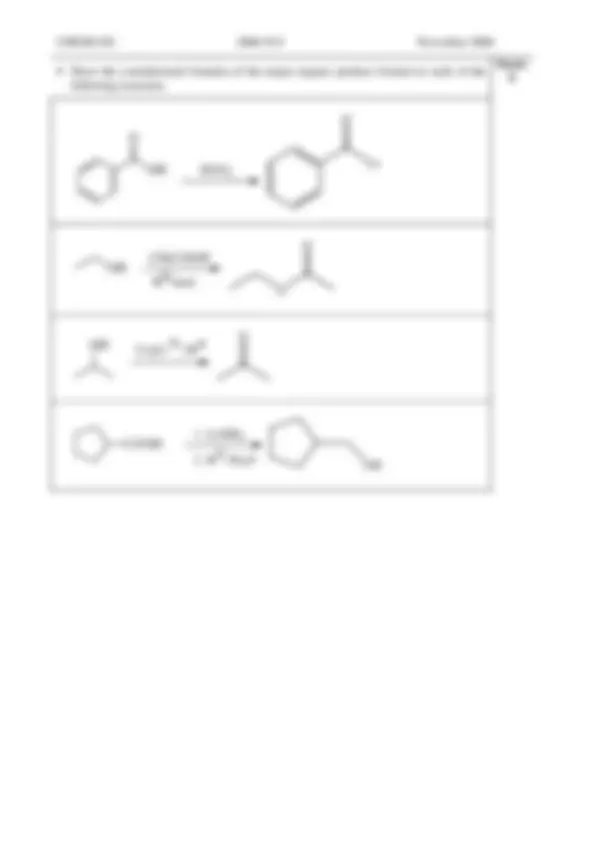
Draw the structure of the organic product(s) formed when each of the following compounds is treated with 4 M sodium hydroxide.
Typology: Exams
1 / 39

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
































CHEM1102 2014 - J- 8 June 2014
Marks 4
hot 3 M NaOH
Cl
CHEM1102 2014 - J- 9 June 2014
Marks 7
Using one stereogenic centre you have identified, draw the ( R )-configuration of that centre.
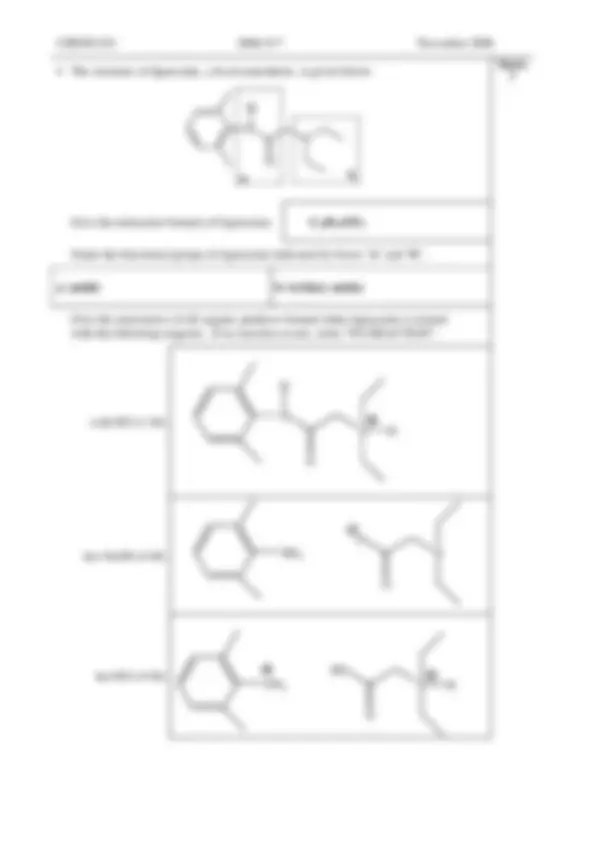
How many stereoisomers are there of methylphenidate? Describe the relationships between these isomers.
4 isomers: there are 2 pairs of enantiomers: Each isomer has 1 enantiomer and 2 diastereoisomers
Give the products formed when methylphenidate is hydrolysed with 4 M HCl.
methylphenidate
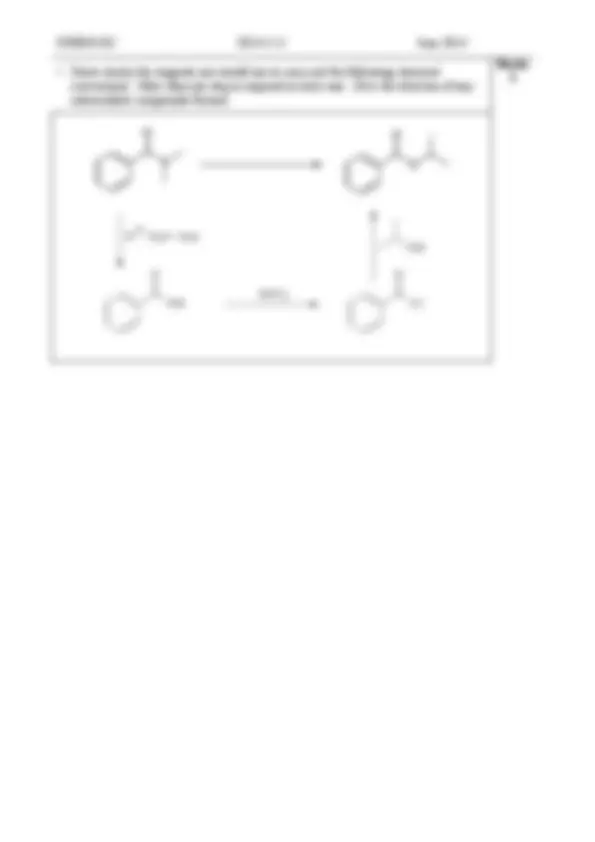
CHEM1102 2014 - N- 8 November 2014
Marks 1
STARTING MATERIAL REAGENTS/CONDITIONS
SOCl 2
O
Cl
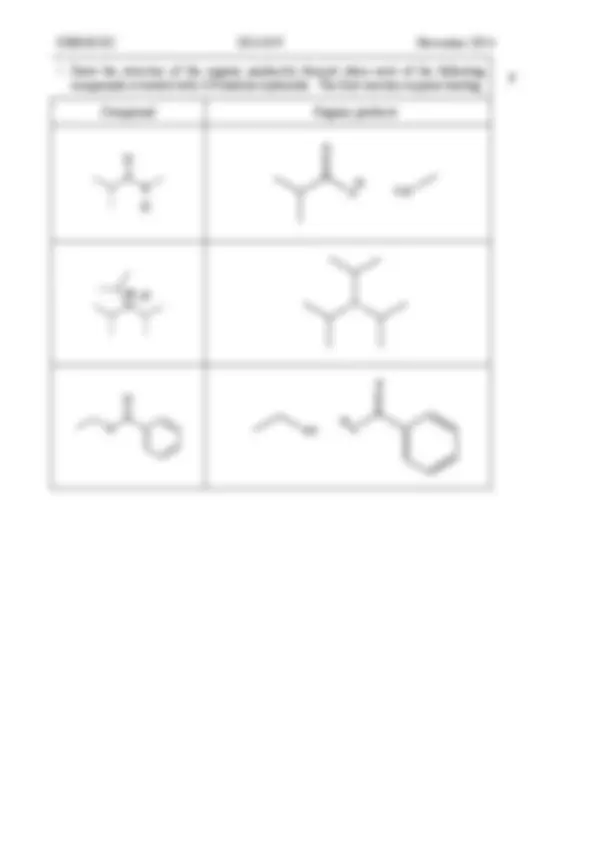
CHEM1102 2014 - N- 9 November 2014
Compound Organic products
O
O
H 2 N
N
OH O
O
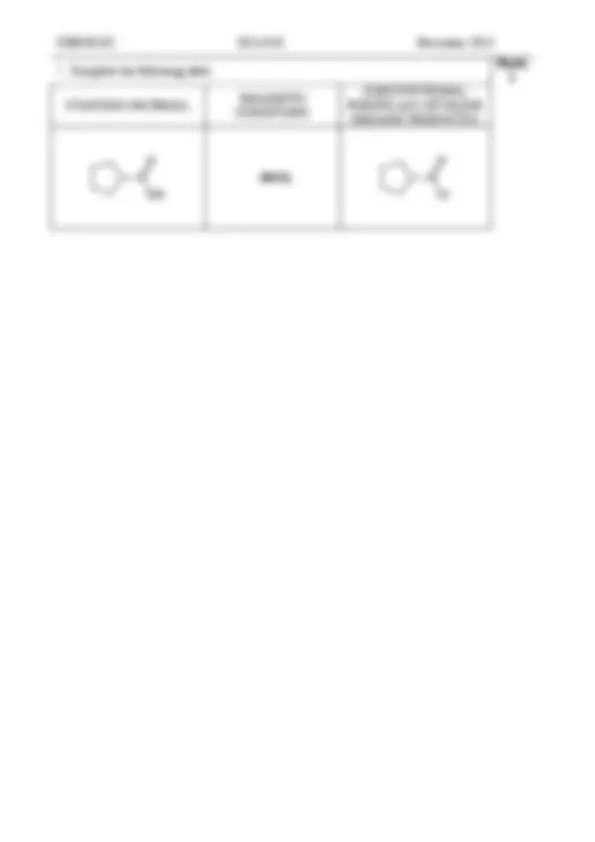
CHEM1102 2013 - J- 14 June 2013
Marks 6
Indicate the hybridisation of the two oxygen atoms in the starting materials.
acid chloride: sp^2 water: sp^3
THE REMAINDER OF THIS PAGE IS FOR ROUGH WORKING ONLY.
CHEM1102 2013 - N- 8 November 2013
Marks 1
SOCl 2
CHEM11 02 2013 - N- 12 November 2013
Arrange these compounds in order of increasing acidity. Explain your reasoning.
Marks 3
Ethanol is the weakest acid as its conjugate base is not resonance stabilised. Phenol is a stronger acid as its conjugate base is resonance stabilised – the negative charge can be delocalised into the aromatic ring as shown below.
There is even greater resonance stabilisation for the acetate ion (the conjugate base of acetic acid), as the negative charge is delocalised onto the electronegative oxygen atoms (as opposed to the carbon atoms in the case of phenol).
CHEM11 02 2013 - N- 13 November 2013
Marks 3
CHEM1102 2012 - J- 10 June 2012
Marks 7
Cr 2 O 72 –^ / H+
H+^ catalyst / heat
(CH 3 ) 2 NH / heat
CHEM1102 2012 - J- 12 June 2012
Marks 6
Give the products when molecule ( M ) is hydrolysed by heating it with 6 M HCl. Make sure you show the products in their correct ionisation states.
CHEM1102 2012 - N- 10 November 2012
Marks 1
SOCl 2
CHEM1102 2012 - N- 11 November 2012
Marks 4
Compound Organic Product(s)
CHEM1102 2010-N-9 November 2010
SOCl (^2)
Cl
H / H 2 O / heat
CHEM1102 2010-N-10 November 2010
Marks 5