




















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
BIOLOGY COMREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT TEST QUESTIONS WITH VERIFIED ANSWERS RATED 100% 1. True or False: A virus is considered a microorganism. False. Viruses are not living and as such are not considered microorganisms. Viruses can, however, be classified as microbes, a more general term that includes microorganisms and viruses. 2. What is the smallest biological unit of life? A cell. 3. At a generalized level, all cells are comprised of what? Macromolecules* *A student may also answer: Proteins, Lipids, Nucleic acids and Polysaccharides but they must answer with all four to be fully correct. 1. How many dif
Typology: Exams
1 / 34

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!



























True .
. True or False: A defining characteristic of Protista is the inability of colonies to form tissue layers.
A, C and D all contain chitin.
Molds
Yeast
Bacteria A. Mushrooms that apply.
Protista C. Fungi
Plantae
Animalia
. Which of the following microorganisms are considered to be Eukarya? Select all that apply.
temperatures and even oxygen-poor conditions. True. Archaea can often be found in harsh conditions such as high salt levels, high acid conditions, high True or False: Archaea is noted for its ability to survive under harsh conditions.
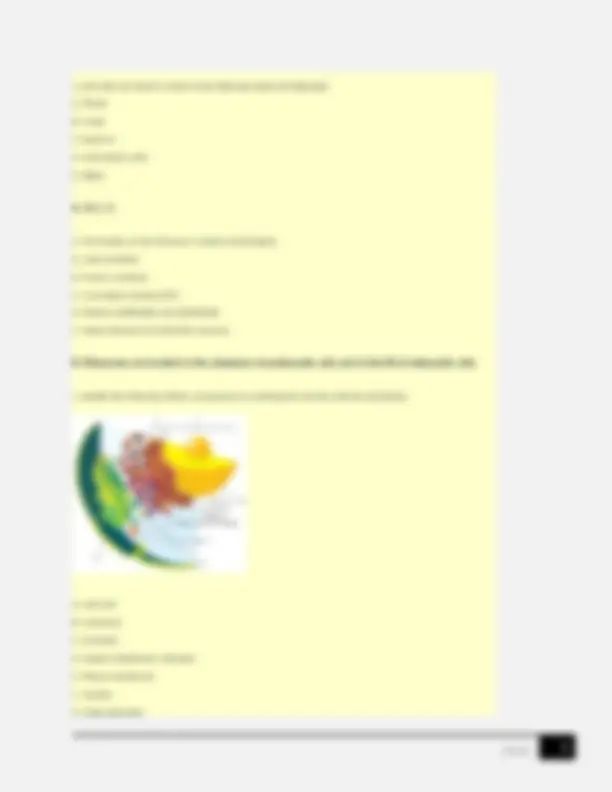
G. Golgi apparatus F. Nucleus E. Plasma membrane D. Rough endoplasmic reticulum C. Centriole B. Lysosome A. Cell wall
E. Algae D. Mammalian cells C. Bacteria B. Fungi A. Plants