






































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
BIOLOGY COMREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT TEST QUESTIONS WITH VERIFIED ANSWERS RATED 100% 1. True or False: A virus is considered a microorganism. False. Viruses are not living and as such are not considered microorganisms. Viruses can, however, be classified as microbes, a more general term that includes microorganisms and viruses. 2. What is the smallest biological unit of life? A cell. 3. At a generalized level, all cells are comprised
Typology: Exams
1 / 51

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!












































False. Fermentation only reduces NADH back to NAD+
C and D. The TCA cycle produces an abundance of reduced electron carriers (NADH and FADH 2 ).
C- Oxioreductaces D- Hydrolases E- Ligases F- Isomerases 1D 1. A-B + H2O → A-OH + B-H Hydrolases 2F 2. A-B→ B-A Isomerases 3E 3. A + B → A-B Ligases 4A 4. A-B → A + B Lyases
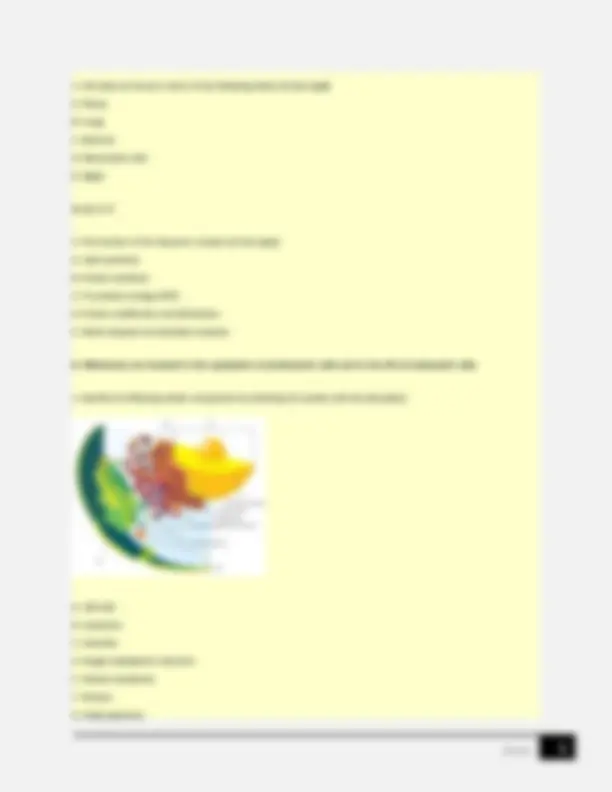
A. Stage B. Fine Adjustment Knob C. Iris Diaphragm D. Neck E. Condenser Lens F. Eyepiece G. Objective H. Base I. Coaxial Controls 1F 2D 3B 4G 5A 6H