Download BIOD 151 Module 4: Problem Set: Essential Human Anatomy & Physiology I w/Lab - Burtt. and more Quizzes Anatomy in PDF only on Docsity!
Module 4 : Problem Set: Essential Human Anatomy & Physiology
I w/Lab - Burtt - 2025E
Attempt History
Attempt Time Score LATEST Attempt 1 56 minutes 5 out of 5 Submitted Jun 17 at 1:24pm This attempt took 56 minutes. Question 1 Anatomy of the Skeleton Part I
- What is the function of the flat bones?
- Describe the shape of a long bone and what its design allows.
- Name the five basic bone shapes.
- What term best describes a hollow chamber in bone, usually filled with air?
- True or false: A sulcus is a raised ridge in bone.
- What division of the skeleton lies along the midline?
- True or false: Fontanelles are present in adults.
- What two bones of the cranium lie primarily within the skull?
- True or false: The frontal bone is a paired bone of the cranium.
- Which bone contains the foramen magnum?
- What is the purpose of the foramen magnum?
- Review bone landmarks on the occipital bone.
- Sinusitis is an infection of the.
Your Answer:
- form the roof of the skull to protect the brain 2.. Long bones are long and thin, designed to support body weight and enable movement
- Long Bones, flat bones, Short bones, Irregular bones, Seasmoid bones
- Sinus
- depressions in bone
- axial
- F
- cranium and facial
- F
- occipital bone
- which the spinal cord passes to become the brain stem
- the soft tissues inside the sinuses
- Produce red blood cells; protection of internal organs (skull protects the brain).
- Long and thin; designed to support body weight and enable movement
- Long, flat, short, irregular, and sesamoid.
- Sinus
- What is the function of the nasal conchae?
- What are the only unpaired bones of the facial skeleton?
- What bone forms the anterior portion of the hard palate?
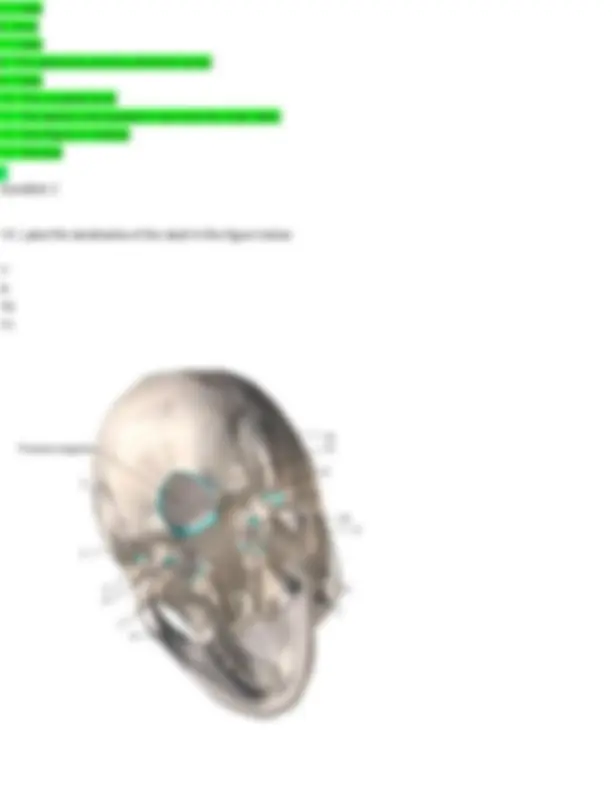
- Label all the bones of the cranium and facial skeleton.
Your Answer:
- swirl the air as it is breathed in through the nasal passages, helping to warm and humidify the air before it
enters the lower respiratory system
- mandible and vomer
- maxillae
- 1 - Mastoid foramen
4 - Carotid canal 10 - Carotid canal 11 - External acoustic meatus
- The nasal conchae act to swirl the air as it is breathed in through the nasal passages, helping to warm and
humidify the air before it enters the lower respiratory system.
- The mandible and the vomer
- The maxilla
- See figures in module.
Question 3
- True or false: A typical spine is completely straight when standing vertically.
- True or false: The vertebral body is located anteriorly and can be palpated along the surface of the back.
- The vertebrae fit together to protect the , located in the vertebral canal.
- True or False: A typical thoracic vertebra has a bifid spinous process.
- What is the purpose of transverse foramina in cervical spinal vertebrae?
- What region of the spine contains costal facets?
- What is the purpose of costal facets?
- Which region of the spine has the largest vertebral bodies?
- The line along the midline of the sacrum is called the
- True or False: Ribs 11 and 12 have no posterior attachment to the thoracic vertebrae.
Your Answer: False False Spinal cord False Passage of blood vessels Thoracic region. To articulate with ribs Lumbar region Median sacral crest False
- False (note the typical curvatures in a spinal column)
- False (located anteriorly, but the spinous processes are the structures that can be palpated along the surface of
the back)
- The spinal cord
- False
- Passage of vertebral arteries and veins
- Thoracic
- Articulations with ribs
- Lumbar
- Review all bones of the hand.
Your Answer:
- False
30.False
- True
- Scapular landmarks include
Supraspinatus fossa Infraspinatus fossa Subscapular fossa Scapular spine Acromion process Coracoid process Glenoid cavity
- Because the glenoid cavity is shallow and offers little bony stability, relying mostly on ligaments and muscles
(rotator cuff) for joint support.
- Radius
- False
- Humerus landmarks include
Hea Neck Shaft Capitulum Trochlea Medial and lateral epicondyles
- Olecranon process This is the prominent bone palpated at the back of the elbow.
- Interosseous membrane
- Ulna and Radius landmarks include:
Olecranon process Head Shaf Styloid process
- Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate, Hamate
- False
- False
- True
- See figures in module
- The glenoid cavity is very shallow and much smaller than the head of the humerus. The humerus needs to be
held to the shallow glenoid cavity by the rotator cuff muscles and other ligaments
- Radius
- False
- See figures in module of the humerus.
- Ulna
- Interosseous membrane
- See figures in module
- The distal row of carpal bones (from lateral to medial) are: trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate.
- See figures in module of the hand.
Question 5
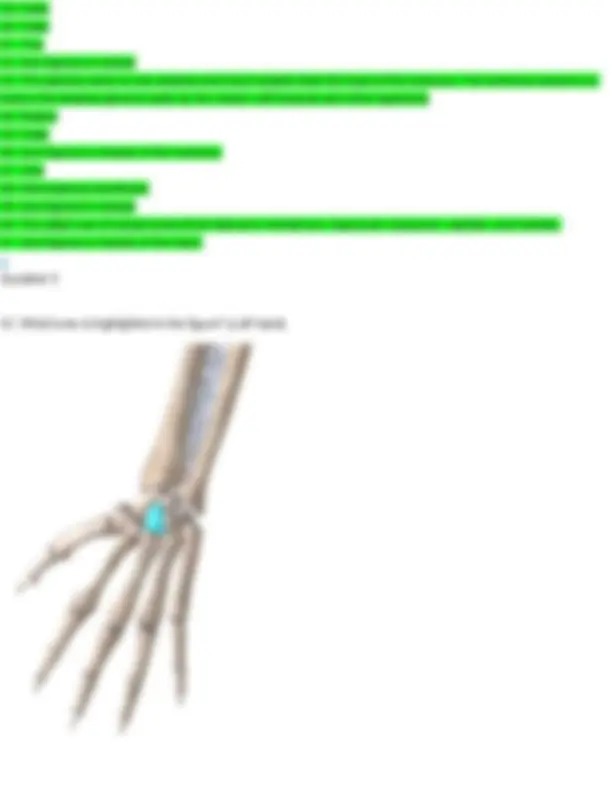
- What bone is highlighted in the figure? (Left hand)
- Review all bone landmarks of the femur.
- What bone lies anteriorly to the femur?
- The medial malleolus of the ankle is a part of what bone?
- Review bone landmarks of the tibia and fibula.
- What bone of the foot is highlighted in blue below (left)?
- Review bones of the foot. Your Answer:
- Metacarpals
- Sacrum
- Iliac crest
- Ilium
- Pubic symphysis
- Female: wider, oval inlet; Male: narrower, heart-shaped
- False
- Linea aspera
- Patella
- Tibia
- Talus
- True or false: Endochondral ossification is the ossification of long bones from hyaline cartilage.
- True or false: Intramembranous ossification is the formation of flat bones from connective tissue.
- This type of fracture occurs when one end of the bone is pushed inside the other.
- This type of arthritis causes the synovial membrane to become inflamed. Your Answer:
- Yellow and red bone marrow — fat storage and blood cell production
- Diaphysis
- Articular cartilage
- Spongy
- Compact
- Osteoclast
- False
- True
- True
- Impacted fracture
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Yellow bone marrow is a fat storage tissue found mainly in long bones. Red bone marrow is found primarily in short and flat bones, primarily to produce red blood cells.
- Diaphysis
- articular cartilage
- Spongy bone
- Compact
- Osteoclasts
- False
- True
- True
- Impacted
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Question 7 Joints and Ligaments
- What type of joint is immovable: Fibrous, cartilaginous or synovial?
- Synovial joints produce what type of fluid?
- The thumb has this type of synovial joint to allow the thumb to cross over the palm.
- The clavicle connects posteriorly to the scapula via what ligament?
- Review all shoulder ligaments.
- The ligament attaches the femur to the ilium.
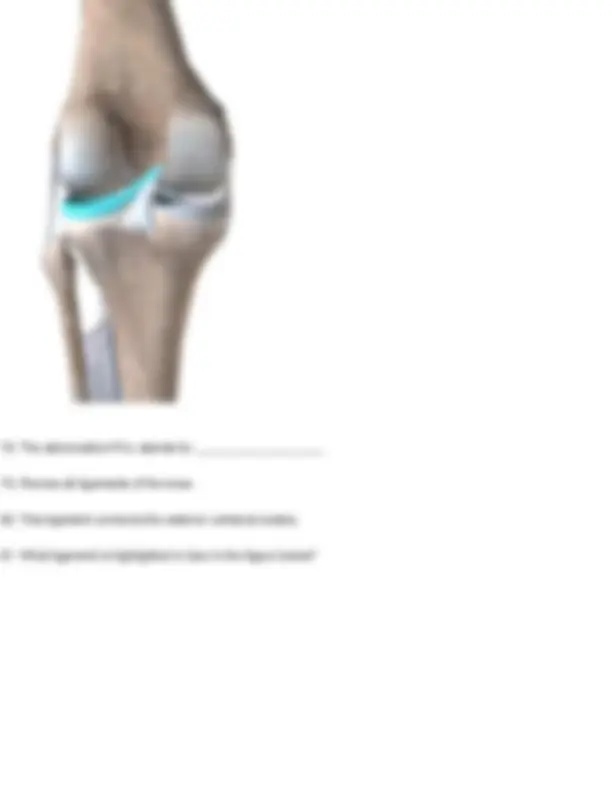
- What ligament is highlighted in blue in the figure below?
- Review all pelvic ligaments.
- What is highlighted in blue in the figure below? (posterior view)
- Why can a herniated disc be painful?
- Review all spinal ligaments. Your Answer:
- Fibrous
- Synovial fluid
- Saddle joint
- Iliofemoral ligament
- Coracoacromial ligament
- ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament)
- Posterior Cruciate Ligament
- Patellar, MCL, LCL, ACL, PCL, menisci
- Anterior longitudinal ligament
- Supraspinous ligament
- It presses against the spinal cord or spinal nerve
- Because it presses against the spinal cord or spinal nerves.
- Fibrous joints
- Synovial fluid
- Saddle joint
- Acromioclavicular ligament
- See figure in module
- The iliofemoral ligament
- Iliolumbar ligament (left and right)
- See figure in module
- Lateral meniscus
- Posterior cruciate ligament
- See figure in module.
- Anterior longitudinal ligament.
- Supraspinous ligament
- Pain results when the damaged disk presses against the spinal cord or the spinal nerves.
- See figure in module.
Question 8 5 / 5 pts As a reminder, the questions in this review quiz are a requirement of the course and the best way to prepare for the module exam. Did you complete all questions in their entirety and in your own words? Your Answer: yes