









Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An introduction to operating systems, their functions, and their evolution over time. It explains the role of an operating system as an interface between a computer user and hardware, and the core components of an operating system. It also discusses the functions of an operating system, including memory management, processor management, device management, file management, network management, security, and control over system performance. The document concludes with a discussion of computer-system operation and memory layout for multiprogrammed systems.
Typology: Summaries
1 / 16

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!










U U U
. Execute user programs and make solving user problems easier . Make the computer system convenient to use . Use the computer hardware in an efficient manner
U Computer system can be divided into four components:
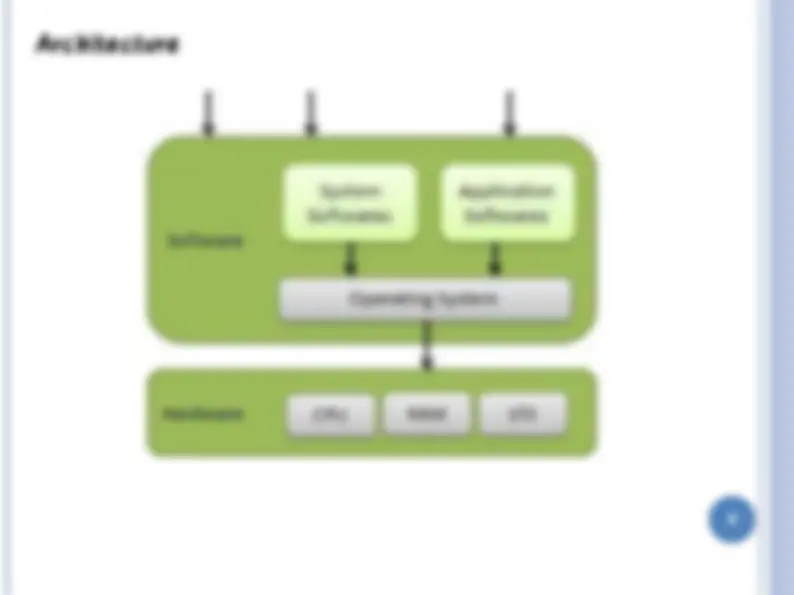
. Hardware – provides basic computing resources U CPU, memory, I/O devices . Operating system U Controls and coordinates use of hardware among various applications and users . Application programs – define the ways in which the system resources are used to solve the computing problems of the users U Word processors, compilers, web browsers, database systems, video games . Users U People, machines, other computers
U Depends on user the point of view U (^) Users want convenience, and
. Don’t care about U (^) But shared computer such as or must keep all users happy U Users of dedicate systems such as have dedicated resources but frequently use shared resources from U Handheld computers are resource poor, optimized for usability and battery life U Some computers have little or no user interface, such as embedded computers in devices and automobiles
. Manages all resources . Decides between conflicting requests for efficient and fair resource use
. Controls execution of programs to prevent errors and improper use of the computer
. Typically stored in ROM or EPROM, generally known as . Initializes all aspects of system . Loads operating system kernel and starts execution
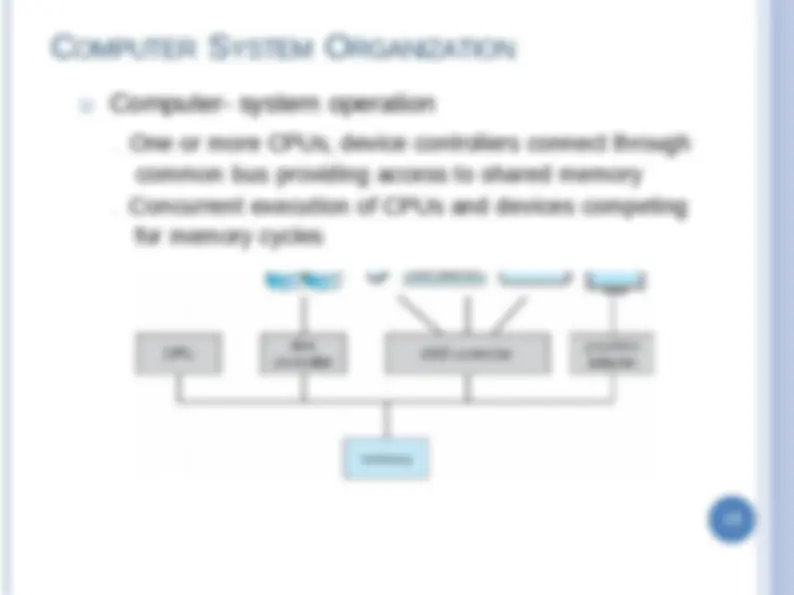
. One or more CPUs, device controllers connect through common bus providing access to shared memory . Concurrent execution of CPUs and devices competing for memory cycles
MEMORY LAYOUT FOR MULTIPROGRAMMED SYSTEM