










































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Chapter 2 PPT Material Type: Notes; Class: Managerial Accounting; Subject: Accounting; University: Minnesota State University-Mankato; Term: Forever 1989;
Typology: Study notes
1 / 58

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!



















































Hey, we’re Dashboard Confessional. Remembering what you learned in Financial Accounting will help with this chapter!
What’s up with costs? These are important facts.
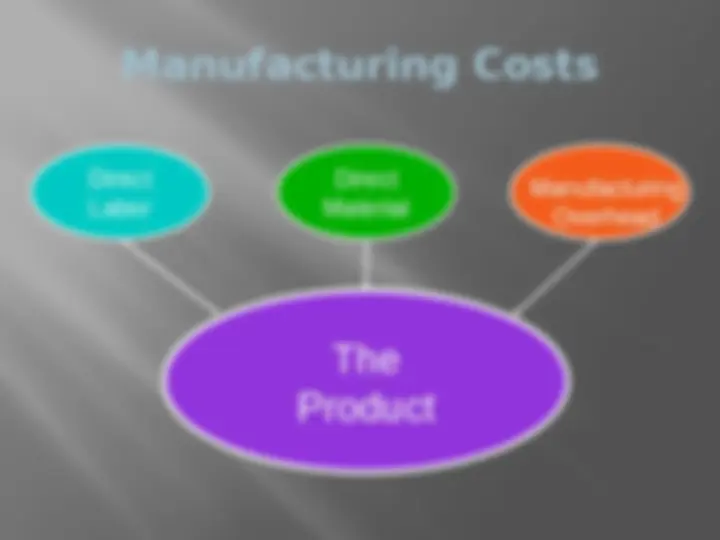
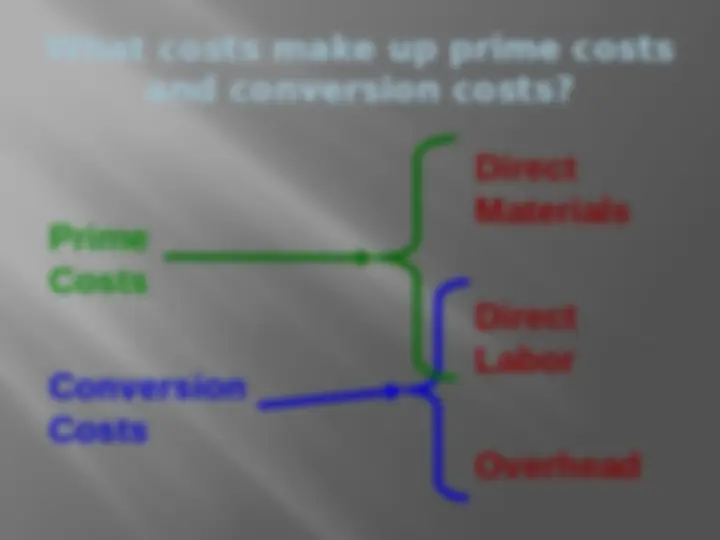
Manufacturing Costs The Product Direct Labor Direct Material Manufacturing Overhead
Define the three components of producing a product. Raw Materials
Cost of salaries, wages, and fringe benefits for personnel who work directly on manufactured products. Direct Labor Example: Wages paid to an airplane assembly worker. Example: Wages paid to an airplane assembly worker.
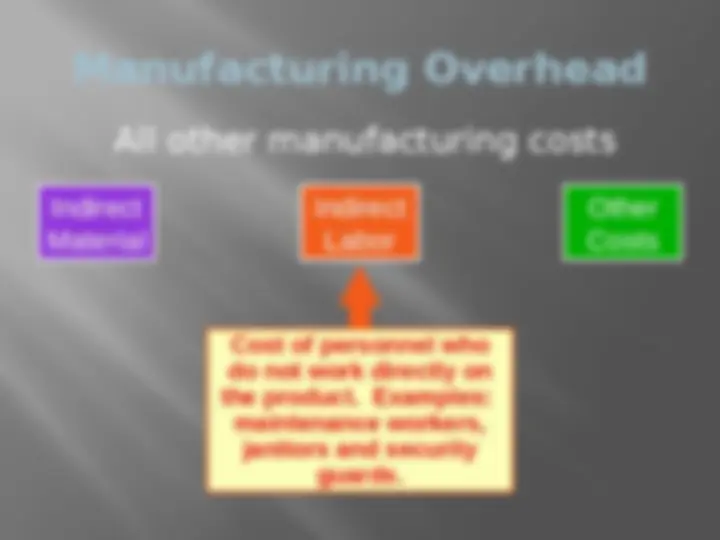
Manufacturing Overhead All other manufacturing costs Materials used to support the production process. Examples: lubricants and cleaning supplies used in an airplane assembly plant. Indirect Labor Indirect Material Other Costs
Manufacturing Overhead All other manufacturing costs Examples: depreciation on plant and equipment, property taxes, insurance, utilities, overtime premium, and unavoidable idle time. Indirect Labor Indirect Material Other Costs
Product Cost Recap: An Automobile Example
How to calculate product cost in total and per unit. Calculation: Direct materials Direct labor Overhead Total product cost $ 38, 24, 57, $120, Per-unit product cost = $120,000 / 24,000 = $ Therefore, one pair of jeans cost $5 to produce.
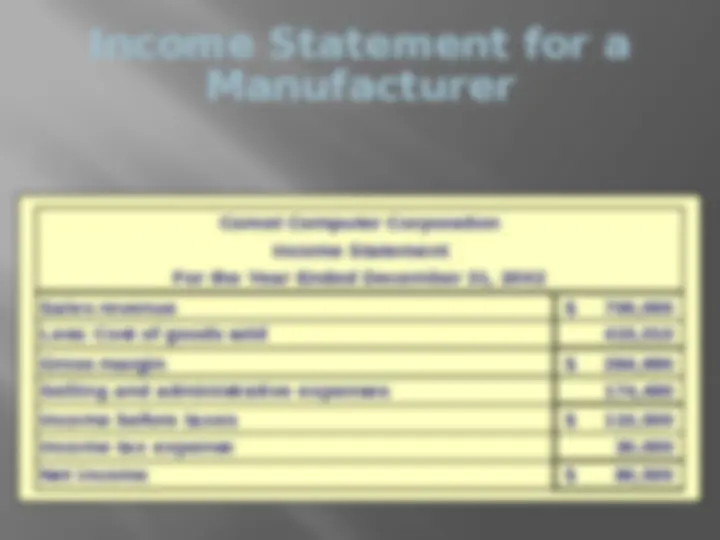
Cost Classifications on Financial Statements – Balance Sheet Merchandiser
Cash Receivables Prepaid Expenses Merchandise Inventory Manufacturer Current Assets Cash Receivables Prepaid Expenses Inventories Raw Materials Work in Process Finished Goods
Manufacturer Current Assets Cash Receivables Prepaid Expenses Inventories Raw Materials Work in Process Finished Goods Cost Classifications on Financial Statements – Balance Sheet Partially complete products – material to which some labor and/or overhead has been added. Merchandiser Current Assets Cash Receivables Prepaid Expenses Merchandise Inventory
Manufacturer Current Assets Cash Receivables Prepaid Expenses Inventories Raw Materials Work in Process Finished Goods Cost Classifications on Financial Statements – Balance Sheet Merchandiser Current Assets (^) Cash (^) Receivables Prepaid Expenses (^) Merchandise Inventory Completed products awaiting sale.
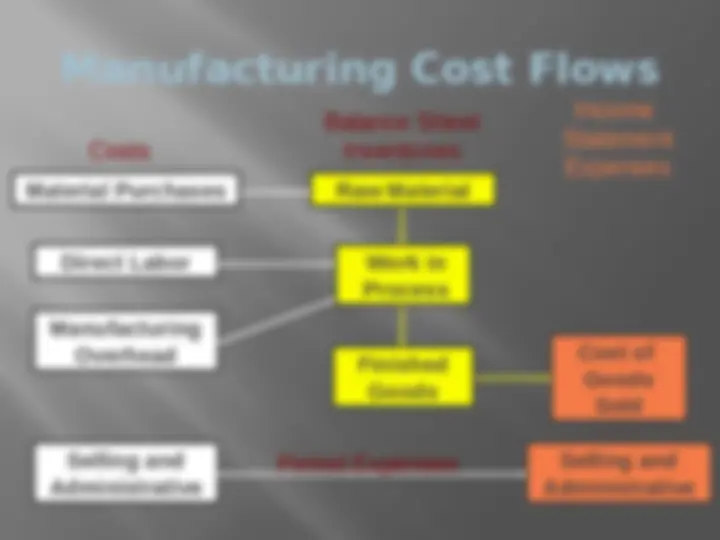
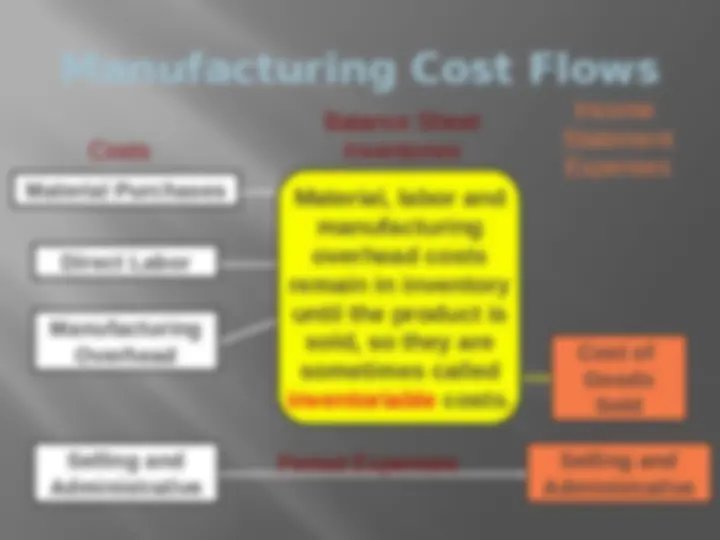
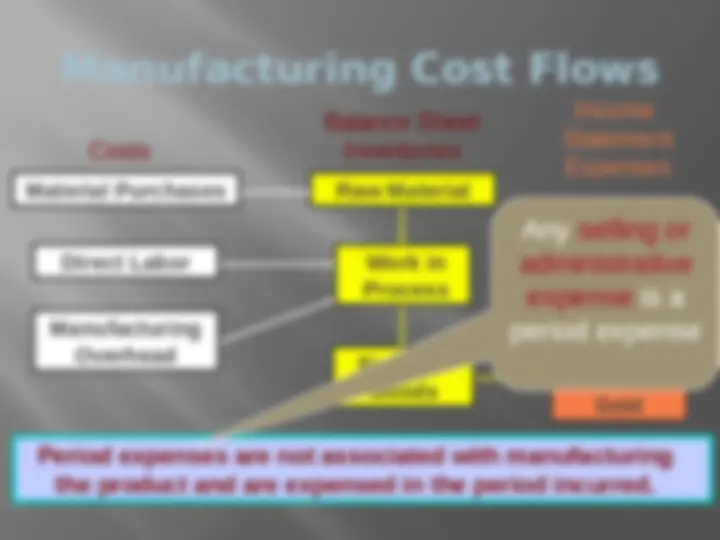
Manufacturing Cost Flows Selling and Administrative Selling and Administrative Period Expenses Manufacturing Overhead Raw Material Work in Process Finished Goods Cost of Goods Sold Material Purchases Direct Labor Balance Sheet Costs Inventories Income Statement Expenses Material, labor and manufacturing overhead costs remain in inventory until the product is sold, so they are sometimes called inventoriable costs.
Manufacturing Cost Flows Selling and Administrative Selling and Administrative Period Expenses Period expenses are not associated with manufacturing the product and are expensed in the period incurred. Manufacturing Overhead Raw Material Work in Process Finished Goods Cost of Goods Sold Material Purchases Direct Labor Balance Sheet Costs Inventories Income Statement Expenses Any selling or administrative expense is a period expense