


























Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
ATI- TEAS 7 | 248 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS | 2025-2026 | GRADED A+
Typology: Exams
1 / 47

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!








































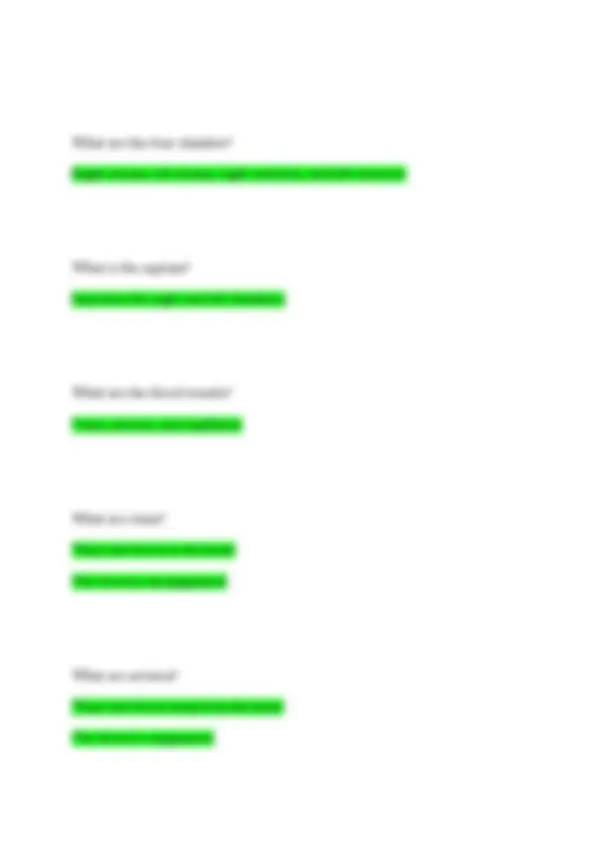
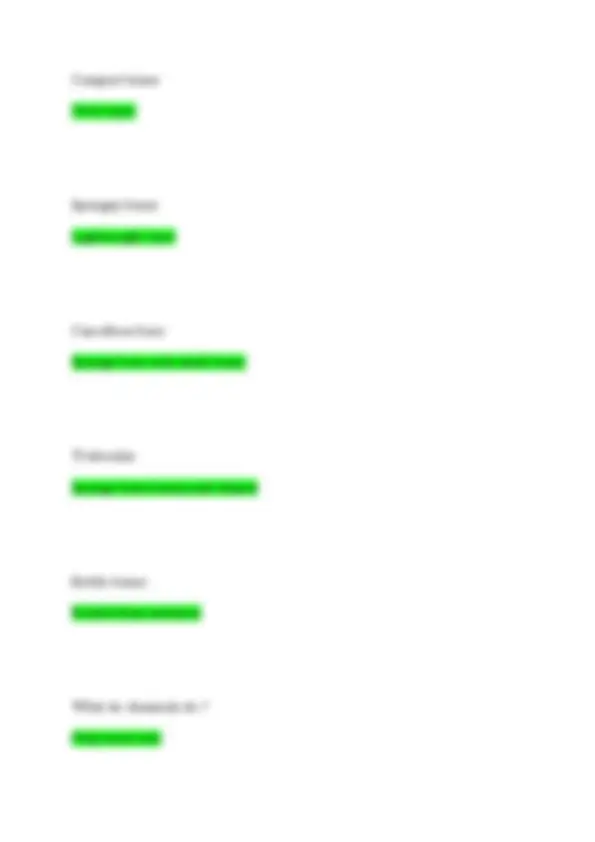
What is the respiratory system responsible for? Taking in oxygen from the environment and releasing carbon dioxide What are the structures of the respiratory system? Mouth, nose, nostrils, throat, larynx, thracea, bronchi, bronchiole, right lung, and left lung What does the nose do? Let in oxygen and let out co What is the larnyx? Voice box What is the trachea? Windpipe
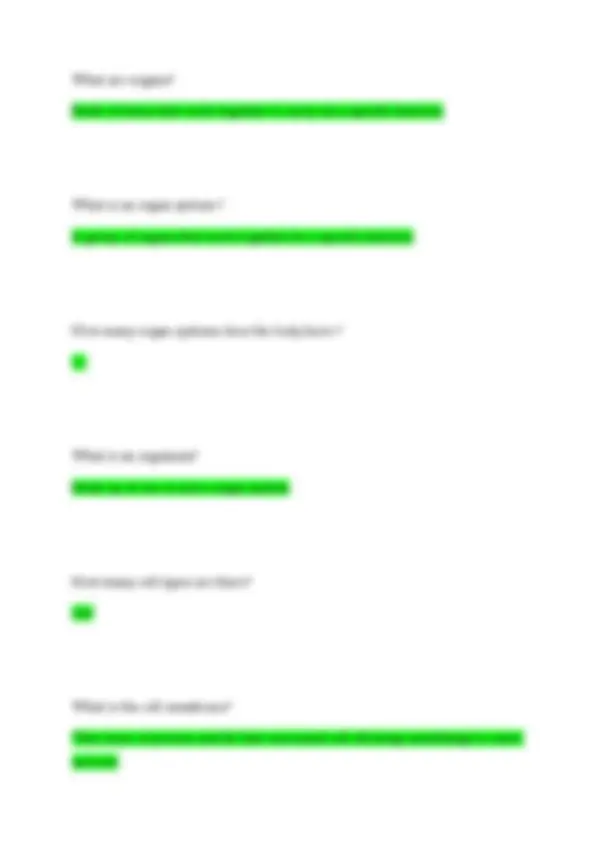
What is is the bronchioles? Extension of the bronchi What are alveoli? Sacs at the end of each bronchoiles What is. The function of the respiratory system?
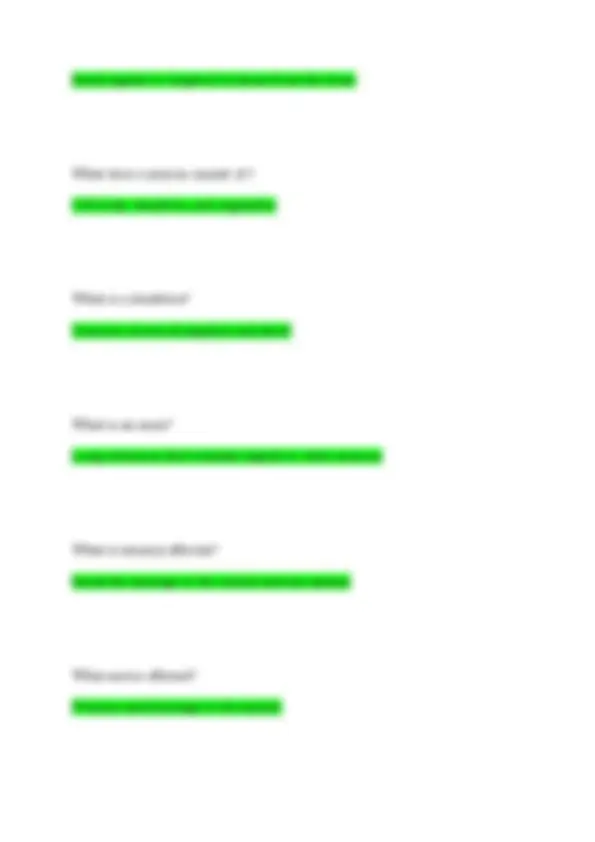
What are capillaries? They connect veins and arteries What is the function of the cardiovascular system? Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to cells and carbon dioxide and waste away from the cells. Regulate b/p, maintain body temp, fight infection, transport hormones What is the contraction of the heart? Systole (lub) sound What is the relaxation of the heart? Diastole (dub) sound What is the is the mitral valve closing? When the heart contraction
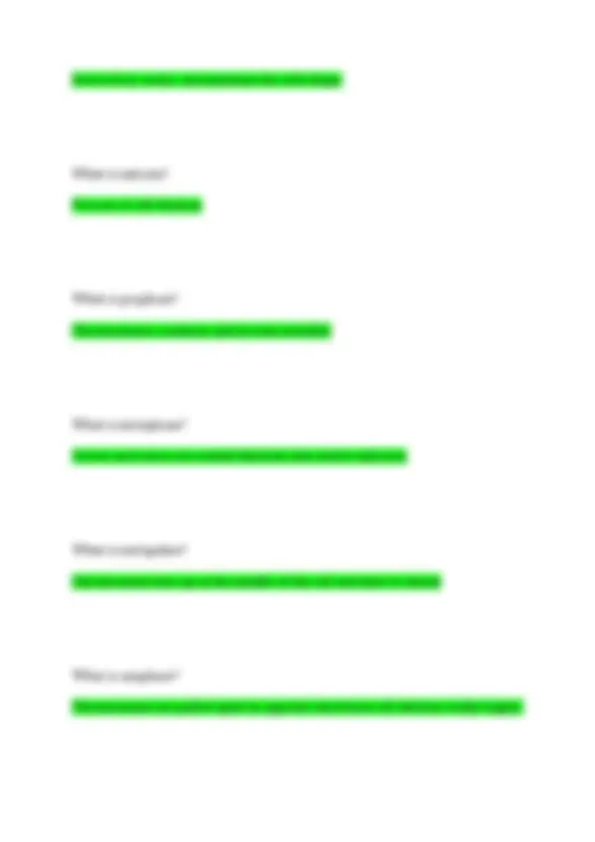
When is the semilunar valve closing? When diastole relax What is the blood flow throught the heart? Superior venna cava to the inferior venna cava to the right atrium to the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle to the pulmonary semilunar valve to the pulmonary artery to the left atrium to the mitral valve to the left ventricle to the aortic valve to the aorta What does the digestive system consist of? Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestines, large intestines, rectum What organs are included in the large intestine? Cecum and colon What does the large intestine do? Absorb water and electrolytes
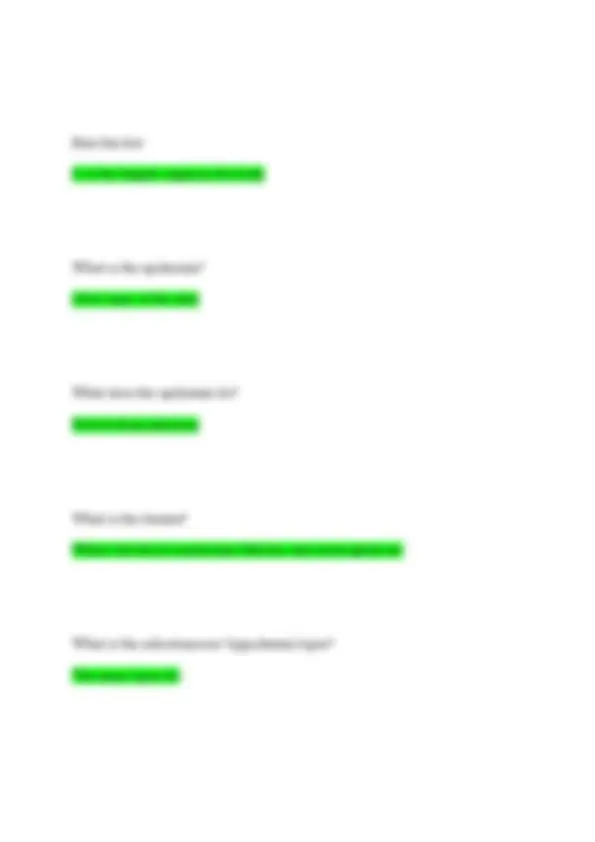
What is glucogon? Produced in the pancreas to regulate glucose What is bile? Produced in the liver, stored in the gallbladder, breaks down fat in the small intestine> What are the two parts of the nervous system? Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system What is the central nervous system? Consist of the brain and spinal cord. This is where all communication and action occur What is the peripheral nervous system? Nerves that break off from the spinal cord and supply the body with nerves. What does the peripheral nervous system do?
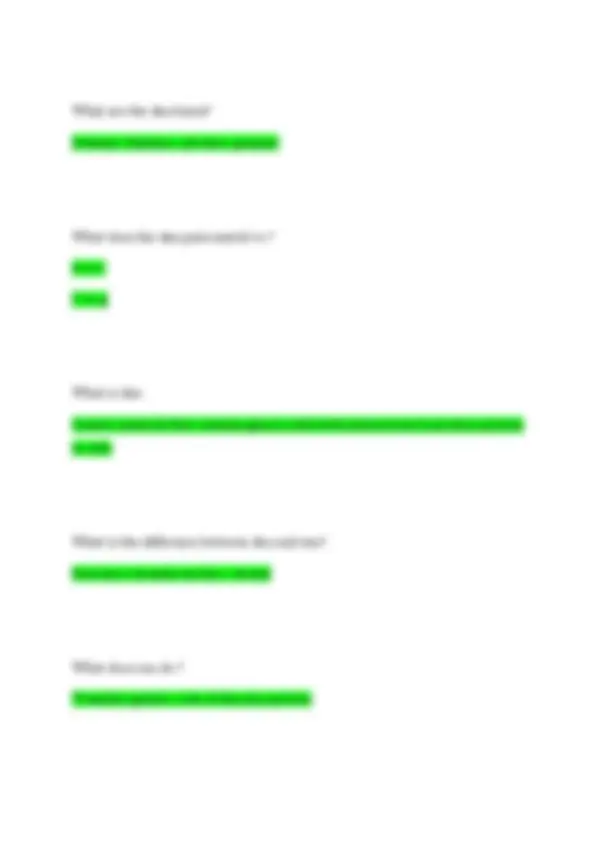
Sends signals to targeted locations from the brain What does a neuron consist of? Cell body, dendrites, and organelles What is a dendrites? Generate electrical impulses and short What is an axon? Long extension that transmit signals to other neurons What is sensory afferent? Sends the message to the central nervous system What motor efferent? Neurons send message to the muscle
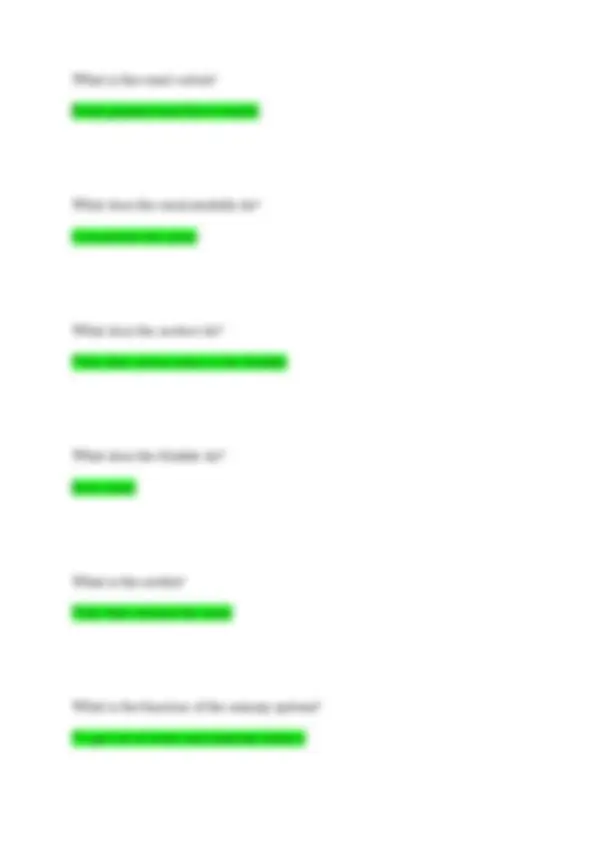
What controls out muscles? Nerves They originate in the brain the to the spinal cord, then to the axon, then to the muscle nerve, then to the muscle fiber What is the skeletal muscle? Is is attached to the bones and responsible for movement What is the cardiac muscle? It is found in the heart and pumps blood throughout the body Is skeletal muscle voluntary or involuntary? Voluntary Is cardiac muscle voluntary or involuntary? Involuntary What is the smooth muscle?
Found in organs and vessel walls Stomach, small intestine, blood vessel (weakest of all ) Is smooth muscle voluntary or involuntary? Involuntary What are testies? Oval shaped organs the produce sperm and testosterone What is the epididymis? Long coiled tube that stores and transports sperm What is the vas deferens? Long this tube that carries sperm from epididymis to semi vesicle What is the prostate? Round gland that produces fluid that helps transport sperm
What is the vagina? Long canal that carries blood, muscoal tissue from the uterus during a period. Passageway for intercourse and sperm, and birth canal. What is a vulva? External labia, clitoris, uretha What is fhs? Stimulating growth for eggs What does estrogen do? Regulates menstrual cycle What does testosterone check? Production of sperm What is the integumentary system made of? Skin, nails, hair, and sweat glands
Skin fun fact It is the largest organ in the body What is the epidermis? Otter layer of the skin What does the epidermis do? Protect from infection What is the dermis? Where the blood vessels hair follicles, and sweat glads are What is the subcutaneous/ hypodermis layer? The inner layer fat
What is calcitonin? Regulate calcium What is thyroxine? Regulate metabolism What does the pituitary gland produce? Growth hormone prolactin What does the parathyroid gland produce? Parathyroid hormone (pth) , regulate calcium in the blood What does the thymus gland produce? Produces thymosin, helps develop immune system Wha does the adrenal gland produce? Produce epinephrine, regulate fight or flight
What does the pancreas produce? Insulin and glucagon, regulate blood sugar levels What does the ovaries produce? Estrogen and progesterone, regulate periods What does the testies produce? Testosterone, regulate the development of male reproduction What does the urinary system consist of? Kidneys, renal cortex, renal medulla, urters, bladder, and uretha What do the kidneys do? Filter out blood
What is innate defense? First line of defense What is inflammatory response? Blood vessels dilate, white blood cells and fluid are sent to the targeted area What is a histamines? Increase in blood flow to the area and the number of white blood cells are called phagocytes What are phagocytes? They destroy unknown bacteria What is adaptive system? Second line of defense
What are antigens? Forigen invaders that the body has been exposed to What are helper t cells? White blood cells induced other cells to help bind to the antigen What is the cytotic t-cells? They destroy infected cells What are antibodies? Proteins that help help destroy the antigen What are memory cells? White blood cells that remember a foreign antigen What is passive immunity? Memory cells made by another individual (mother/baby)