

Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Aggregate Expenditures or Keynesian Cross Framework: Study Aid | ECO 230, Assignments of Introduction to Macroeconomics
Material Type: Assignment; Class: Principles of Macroeconomics; Subject: ECO Economics; University: Murray State University; Term: Unknown 1989;
Typology: Assignments
1 / 1

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!

Related documents
Partial preview of the text
Download Aggregate Expenditures or Keynesian Cross Framework: Study Aid | ECO 230 and more Assignments Introduction to Macroeconomics in PDF only on Docsity!
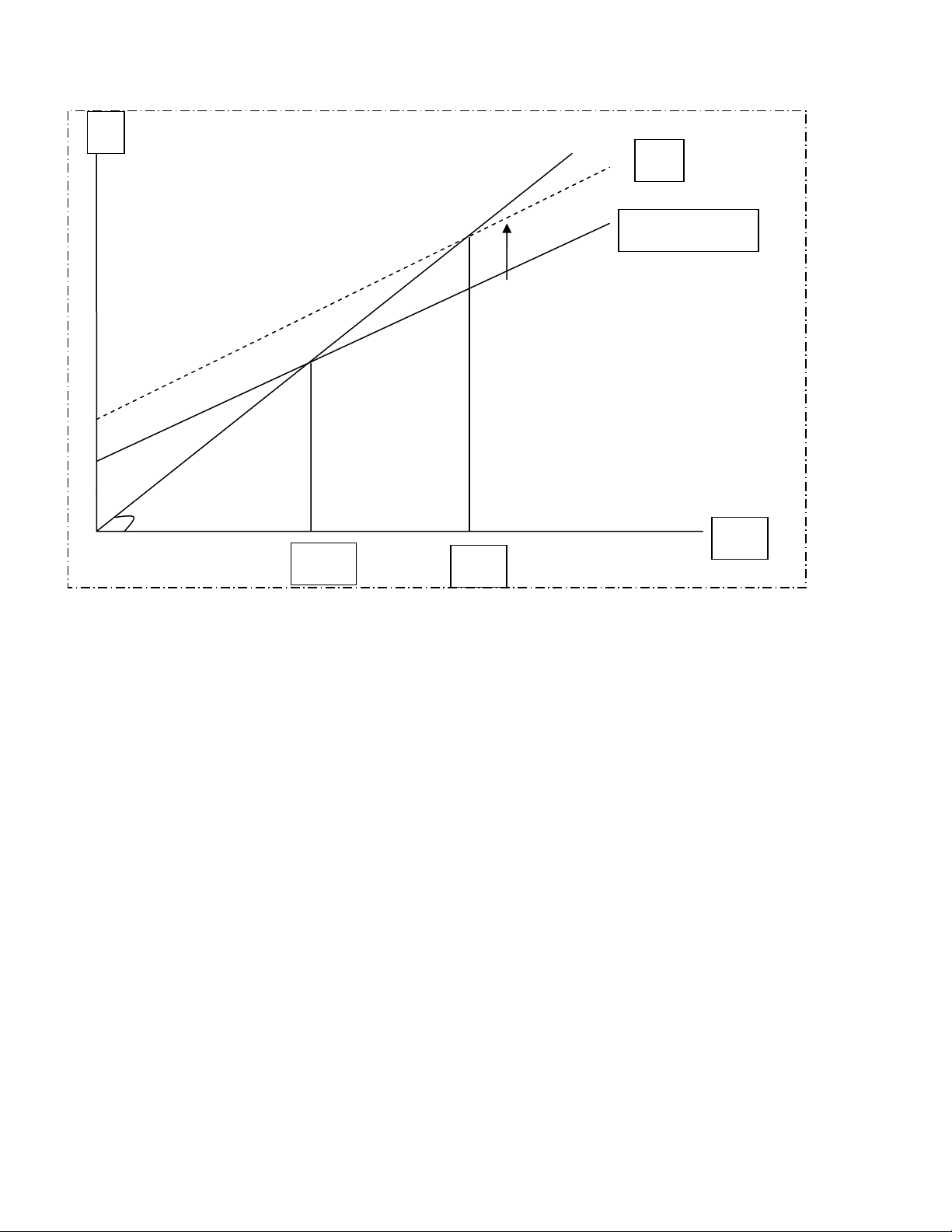
ECO 230 – Study Aid: Aggregate Expenditures or “Keynesian Cross” Framework
E’
C + I + G + Xn
y ye (^) ye’
- y = C + I + G + Xn where y is real GDP/income and C, I, G, Xn are the components of spending (represented by the C + I + G + Xn, or E – for Expenditures - line!)
- Production by business is represented by the 45 degree line. Business produces an amount they believe will be equal to Expenditures for that production (given the current price).
- Equilibrium GDP/income occurs where the two lines intersect.
*4. Equilibrium y can change (by a multiplied amount – to ye’) if the Expenditure curve shifts. Likely reasons (but not he only ones) for shifts include (ceteris paribus!): C – real wealth changes, (stock, bond prices – or the overall price level): W/P inc. => shift E up.
- expectations of future income/inflation inc. => shift E up.
- Taxes decrease => shift E up (by –MPC times change in Taxes)
- Household debt unusually low => shift E up. I – interest rate drops => shift E up.
- Acquisition, operating, maintenance costs of capital drop => shift E up G – increase gov’t. spending => shift E up. Xn – dollar depreciates (FC/$ decreases) => shifts E up.
- tariffs increase => shifts E up.
- foreign incomes increase => shifts E up.
- ∆ye = 1/(1-MPC) times ∆Spending, where MPC is the marginal propensity to comsume = ∆C/∆DI, where DI is disposable income = y-T.

