




Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Solutions to homework problems related to molecular weights and empirical formulas. It includes calculations for determining the molecular weight of various compounds, identifying the empirical formula based on given data, and determining the limiting reagent in a chemical reaction.
Typology: Assignments
1 / 7

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
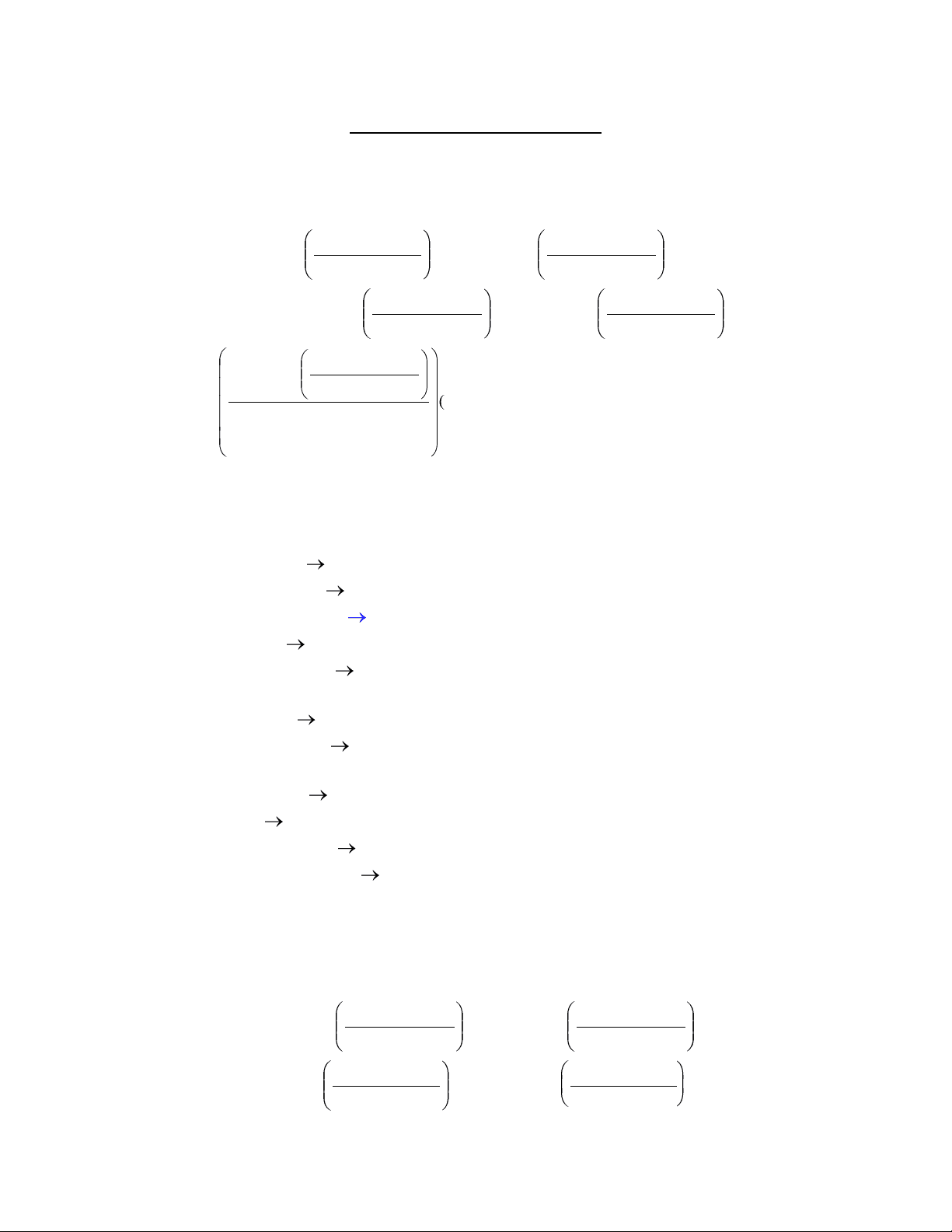



Chapter 3 Homework Solutions
9/9/
b) MW = (2 atomsC) C
C atom
H atom
(1 atomN) N
N atom
O atom
c) %N = ( 100 %)
atom
N N = 18.66 %
b) B 2 S 3 (s) + 6 H 2 O() 2 H 3 BO 3 (aq) + 3 H 2 S(g) c) Pb(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) + 2 NaI PbI2 (s) + 2 NaNO 3 (aq) d) 2 Hg(NO 3 ) 2 (s) 2 HgO(s) + 4 NO 2 (g) + O 2 (g) e) Cu(s) + 2 H 2 SO 4 (aq) CuSO 4 (aq) + SO 2 (g) + 2 H 2 O()
b) C 3 H 6 O() + 4 O 2 (g) 3 CO 2 (g) + 3 H 2 O()
b) Cu(OH) 2 (s) CuO(s) + H 2 O(g) c) C 7 H16 () + 11 O 2 (g) 7 CO 2 (g) + 8 H 2 O() d) 2 C 5 H 12 O() + 15 O 2 (g) 10 CO 2 (g) + 12 H 2 O()
N atom
O atom
b) MWBA = (7 atomsC) C
C atom
1 00794. amu atom
H H
(2 atomsO)
15 9994. amu atom
O O
= 122.1213 amu
c) MWMH = (1 atomsMg) Mg
Mg atom
2 4.3050amu
15 9994. amu atom
O O
(2 atomsH)
1 00794. amu atom
H H
= 58.3197 amu
d) MWurea = (1 atomO O
O atom
1 5.9994amu
C atom
1 2.0107amu
(2 atomsN) 14 0067. amu atom
N N
H H
= 60.0553 amu
e) MWIA = (7 atomsC) C
C atom
H H
(2 atomsO) 15 9994. amu atom
O O
= 130.1849 amu
a) %C = acetylene
C
c C
26.0373 g
mol
place]
b) %H = ascorbicacid
H
H H
176.1241 g
mol
c) %H = amm.sulf.
H
H H
132.1395 g
mol
d) %Pt = cis-platin
Pt
Pt Pt
300.045 g
mol
e) %O = estradiol
O
O O
272.3820 g
mol
f) %C = capsaiscin
C
C C
305.4119 g
mol
Then set up the ratio: EF
cadaverine 102.1781 g/mol
EW
MW = 1 molC5H14N2 per mol(C5H14N2)n
Thus the molecular formula is C 5 H 14 N 2. c) empirical formula = C 9 H 13 O 3 N
EWepinephrine = (9 molC) C
C mol
H mol
O mol
1 5.9994g
N mol
Then set up the ratio: EF
epinephrine 183.2044 g/mol
EW
= 1 molC9H13O3N per mol(C9H13O3N)n
Thus the molecular formula is C 9 H 13 O 3 N.
a) massC = (0.00632 gCO2) C
C CO
C CO
CO 1 mol
1 mol
1 mol = 0.00172 gC
massH = (0.00258 gH2O) H
H H2O
H H2O
H2O 1 mol
1 .00794g 1 mol
2 mol 1 8.0153g
1 mol = 0.000284 gH
massO = 0.00278 g - 0.00172 g - 0.000284 g = 0.00078 gO Then the moles of each substance must be calculated. For C & H you can use the masses you just calculated, but it is better to do it as follows:
molC = (0.00632 gCO2) CO
C CO
CO 1 mol
1 mol
1 mol = 1.44 x 10-^4 molC
molH = (0.00258 gH2O)
1 18.0153 g
2 1
mol mol mol
H2O H2O
H H2O
= 2.86 x 10-^4 molH
molO = (0.00078 gO)
1 mol 15.9994 g
O O
= 4.8 x 10-^5 molO
Now set up the molar ratios.
O
C
4.8x 10 mol
1.44x 10 mol = 3.0 molC per molO O
H
4.8x 10 mol
2.86x 10 mol = 5.96 molH per molO
This yields an empirical formula of C 3 H 6 O. b) By a similar series of steps one finds for nicotine: massC = 3.8868 mg massH = 0.4569 mg massN =0.906 mg molC = 0.3236 mol molH = 0.4533 mol molN = 0.0647 mol 5.00 molC/molN 7.00 molH/molN Empirical formula = C 5 H 7 N. The molecular weight provided is incorrect. It should be 160 ± 5, yielding a molecular
formula of C 10 H 14 N 2.
molMgSO4 = (2.472 gMgSO4) MgSO
MgSO
1 mol = 0.02054 molMgSO
molH2O = (2.589 gH2O) H2O
H2O
1 mol = 0.1437 molH2O
MgSO
H2O
02054 g
1437 mol = 6.997 molH2O per molMgSO4 the formula is MgSO 4 •7H 2 O
a) molCO2 = (0.400 molC6H12O6) C6H12O
CO 1 mol
2 mol = 0.800 molCO
b) massC6H12O6 = (7.50 gC2H5OH) C6H12O
C6H12O C2H5OH
C6H12O C2H5OH
C2H5OH mol
1 mol 46.0684g
1 mol
= 14.7 gC6H12O
c) massCO2 = (7.50 gC2H5OH) CO
CO C2H5OH
CO C2H5OH
C2H5OH mol
4 4.0095g 2 mol
2 mol 46.0684g
1 mol = 7.16 gCO
b) massCO = (0.150 kgFe2O3) CO
CO Fe2O
CO Fe2O
Fe2O Fe2O
Fe2O 1 mol
28.0101g 1 mol
3 mol
1 mol 1 kg
1000 g
= 78.9 gCO c) As in (b), massFe = 105 gFe; massCO2 = 124 gCO d) massreactants = 150 g + 78.9 g = 229 g massproducts = 105 g + 124 g = 229 g massreactants = massproducts
molAl(OH)3 (required) = (0.500 molH2SO4) H2SO
Al(OH) 3 mol
2 mol = 0.333 molAl(OH)
This means that if all of the sulfuric acid were consumed, then 0.333 mol of aluminum hydroxide would be consumed, but you have 0.500 moles of aluminum hydroxide, which is more than this. Thus, if all of the sulfuric acid were used up, you’d have some aluminum hydroxide left over, hence the sulfuric acid is the limiting reagent.
b) molAl2(SO4)3 = (0.500 molH2SO4) H2SO
Al2(SO4) 3 mol
1 mol = 0.167 molAl2(SO4)
massHC2H3O2 (formed) = (7.50 gPb(OAc)2) HC2H3O
HC2H3O Pb(C2H3O2) 2
HC2H3O Pb(C2H3O2) 2
Pb(C2H3O2) 2 1 mol
6 0.0520g 1 mol
2 mol 325.3g
1 mol
= 2.77 gHC2H3O
massPbSO4 (formed) = (7.50 gPb(OAc)2) PbSO
PbSO Pb(C2H3O2) 2
PbSO Pb(C2H3O2) 2
Pb(C2H3O2) 2 1 mol
3 03.3g 1 mol
1 mol 325.3g
1 mol
= 6.99 gPbSO
molBr = (52.92 gBr) Br
Br
1 mol = 0.6623 molBr
molK = molBr = 0.6623 molK
massK = (0.6623 molK) K
K 1 mol
massO = 100.00 g – 52.92 g – 25.89 g = 21.19 gO
molO = (21.19 gO) O
O 15.9994 g
1 mol = 1.324 molO
molar ratio: Br
O
6623 mol
324 mol = 2.0 molO per molBr formula is KBrO 2
First begin with a balanced equation: 2 C 8 H 18 () + 25 O 2 (g) 18 H 2 O() + 16 CO 2 (g)
Now calculate the volume of gasoline needed: Vgas = (225 mi) 20.5mi
1 gal = 11.0 galgas
From this you can calculate the mass of the gasoline and from that the mass of CO 2 produced.
massCO2 = (11.0 galgas) CO
CO C8H
CO C8H
C8H 1 mol
4401 g 2 mol
16 mol 1142 g
1 mol mL
069 g L
1000 mL 1.057qt
1 L gal
4 qt. .
.
= 88,500 gCO2 (or 88.5 kg)